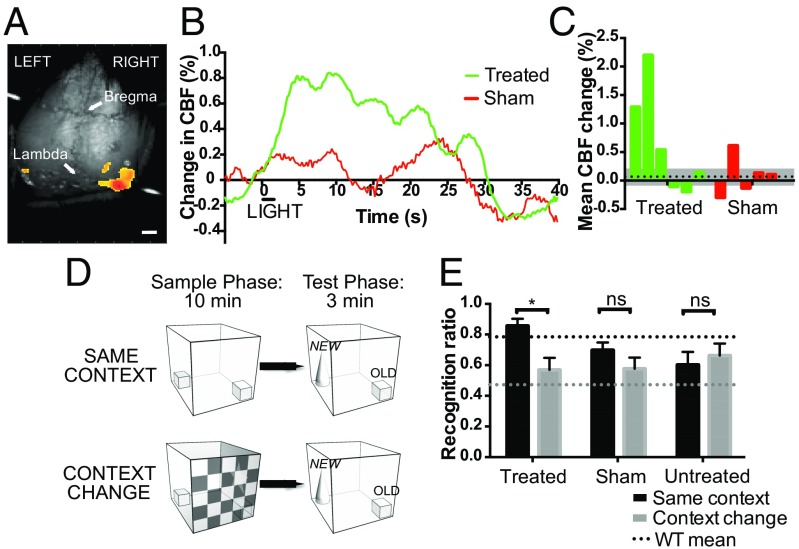
Fig. 4.
Visual responses requiring image-forming vision are generated following melanopsin gene therapy in the degenerate retina. Laser speckle cortical imaging was used to measure changes in visual cortex blood flow following a 2-s, 480-nm light stimulus of 2,000-lx intensity (A). (Scale bar, 1 mm.) OPN4 vector-treated mice showed an appropriate light-dependent peak in cortical blood flow (CBF) compared with sham-injected controls (B; treated, n = 5; sham-injected, n = 4). The mean percentage change in CBF for each animal in the first 10 s after light onset is shown (C). The dashed line indicates mean change in sham-injected animals with SEM (gray). Visual context recognition testing (D): in the “same context” condition, the visual environment is identical in both phases. In the “Context Change” condition, there is a change in visual environment between phases, but all other factors are constant. The recognition ratio is calculated as N/(N + f), that is, time spent exploring the novel object (N) as a fraction of the total time spent exploring both the novel and a familiar (f) object. Thirteen months after OPN4 vector delivery, recognition ratios for the novel object were significantly different in treated mice when the visual environment was the same versus when it was changed, indicating a visual environment-dependent change in behavior (E) (P = 0.04, two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test; dashed line, wild-type mean, *P < 0.05; treated, n = 9; sham-injected, n = 8; untreated, n = 11; ns, nonsignificant).