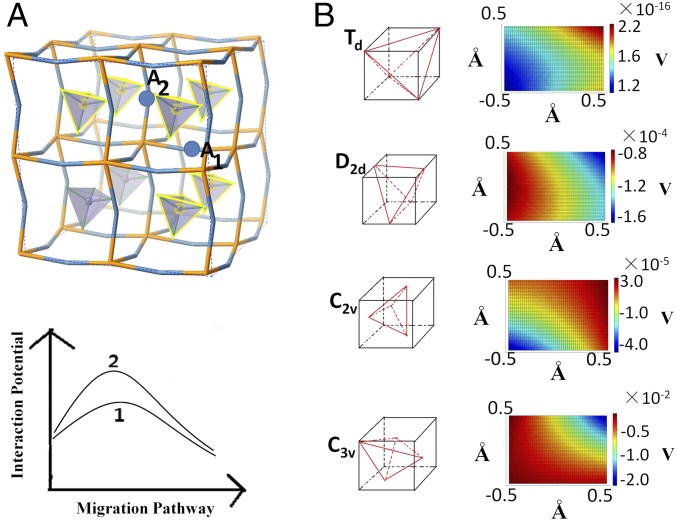
Fig. 2.
(A) The model used to study the relation between the rotation of the BF4− units and the interaction potential felt by the Li+ ion as it migrates from A1 site to A2 site. The four coordinating BF4− units at each site are highlighted in yellow. Curve 1 and curve 2 show two possible potential profiles along the migration pathway created by the rotation of the BF4− units. (B) Calculated potential surfaces in an area of 1.0 × 1.0 Å around the Li+ site for different orientational symmetries of the BF4− tetrahedra. The C3v symmetry generates the lowest potential of the order of −10−2 V. Effect of the translational motions of the BF4− units on the potential surface is shown by the changing color.