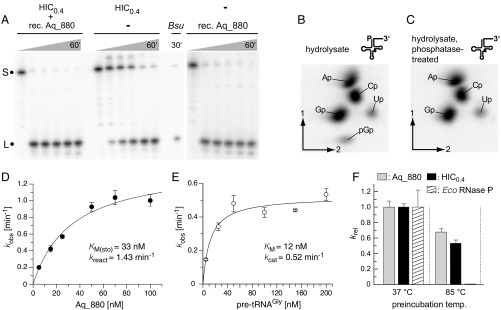
Fig. 2.
(A) Processing of Thermus thermophilus pretRNAGly by the “HIC0.4” fraction [material eluted from a HIC column at 0.4 M (NH4)2SO4; Center], by recombinant Aq_880 (final concentration 0.1 µg/µL) (Right), or by a mixture of both (Left); Bsu, B. subtilis RNase P as positive control; S, the 5′-[32P]-endlabeled pretRNAGly substrate; L, the 5′-leader cleavage product. (B and C) Analysis of the 5′-end of pretRNAGly as processed by recombinant Aq_880 in vitro. PretRNAGly was labeled by in vitro transcription in the presence of [α-32P]GTP and processed with recombinant Aq_880 under standard conditions to nearly completeness. The 5′-mature tRNA product was gel-purified, and a part of the eluate was treated with alkaline phosphatase. Untreated (B) and phosphatase-treated (C) RNAs were subjected to alkaline hydrolysis, and monophosphate and diphosphate nucleosides were resolved by 2D TLC. The pGp bisphosphate (B) is sensitive to phosphatase pretreatment (C) consistent with its origin from the tRNA’s 5′-end. Spot intensities correspond to the number of the respective nucleosides that are followed by a G in the tRNA sequence and, thereby, are radioactively labeled (A, 8; C, 8; G, 9; U, 1). (D) Single-turnover kinetics of recombinant Aq_880 for the processing of pretRNAGly (data points are based on three to six independent determinations for each concentration of Aq_880); error bars are SDs. Kinetic constants and the standard errors of the curve fit are kreact = 1.43 ± 0.14 min−1 and Km(sto) = 33 ± 8 nM. (E) Multiple-turnover kinetics of pretRNAGly processing using 1 nM Aq_880. Results are based on three independent determinations for each pretRNA concentration. Error bars are SDs of the mean. Kinetic constants and the standard errors of the curve fit are kcat = 0.52 ± 0.04 min−1 and Km = 12 ± 4 nM. (F) Thermostability of recombinant Aq_880 (gray bars) or a HIC0.4 fraction containing native RNase P (black bars) in comparison with the E. coli RNase P holoenzyme (white and hatched bars, respectively). RNase P activities were preincubated either at 37 °C or 85 °C before their catalytic activity was determined under single-turnover conditions at 37 °C. Error bars are standard deviations of the mean based on at least three experiments. Note that the activity of E. coli RNase P after preincubation at 85 °C was so low that the corresponding bar to the right of the black HIC0.4 bar does not rise above the baseline.