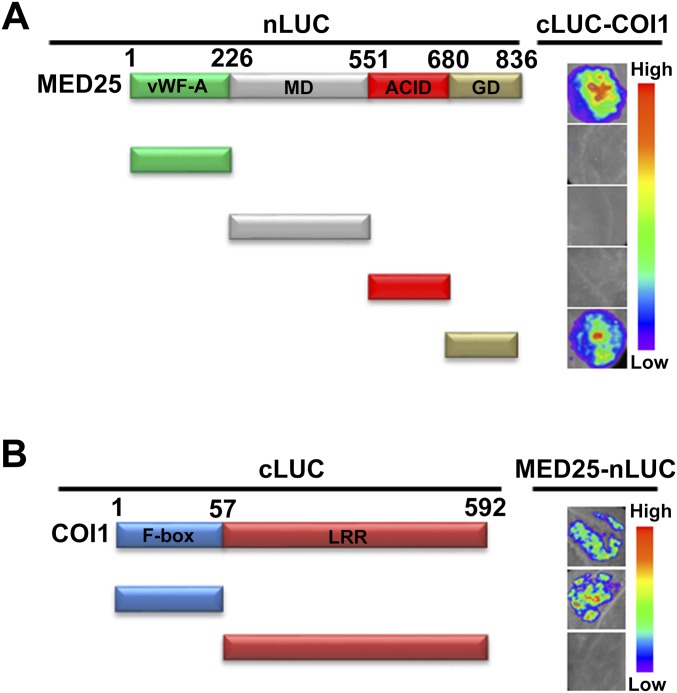
Fig. S2.
Mapping of the protein domains involved in MED25–COI1 interaction using LCI assays. (A) Based on the schematic protein structure of MED25, full-length MED25 or its derivatives (MED25-nLUC or MED25-nLUC derivatives) were tested for interactions with COI1 (cLUC-COI1). N. benthamiana leaves cotransformed with MED25-nLUC or MED25-nLUC derivatives and cLUC-COI1 were imaged 72 h after Agrobacterium infiltration. (B) Based on the schematic protein structure of COI1, full-length COI1 or its derivatives (cLUC-COI1 or cLUC-COI1 derivatives) were tested for interaction with MED25 (MED25-nLUC). N. benthamiana leaves cotransformed with cLUC-COI1 or cLUC-COI1 derivatives and MED25-nLUC were imaged 72 h after Agrobacterium infiltration. ACID, activator-interacting domain; GD, glutamine-rich domain; LRR, leucine-rich repeat; MD, middle domain; vWF-A, von Willebrand factor A domain. In A and B, the pseudocolor bar shows the range of luminescence intensity.