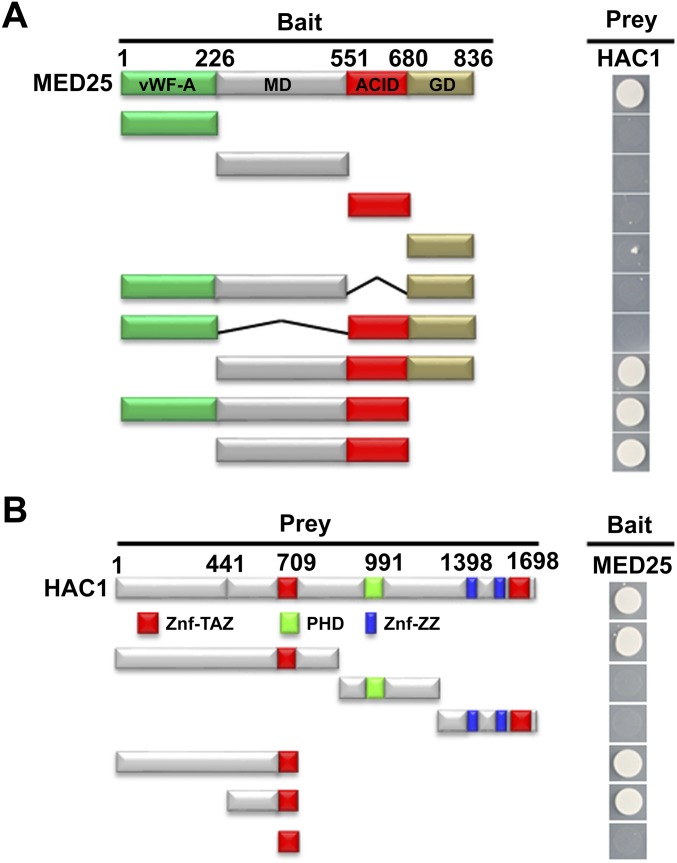
Fig. S4.
Mapping of the protein domains involved MED25–HAC1 interaction using Y2H assays. (A) Based on the schematic protein structure of MED25, full-length MED25 or its derivatives (pGBKT7-MED25 or pGBKT7-MED25 derivatives) were tested for interaction with HAC1 (pGADT7-HAC1). Yeast cells cotransformed with pGBKT7-MED25 or pGBKT7-MED25 derivatives (baits) and pGADT7-HAC1 (prey) were grown on selective media lacking Ade, His, Leu, and Trp (SD/-4) to test protein interaction. (B) Based on the schematic protein structure of HAC1, full-length HAC1 or its derivatives (pGADT7-HAC1 or pGADT7-HAC1 derivatives) were tested for interaction with MED25 (pGBKT7-MED25). Yeast cells cotransformed with pGADT7-HAC1 or pGADT7-HAC1 derivatives (prey) and pGBKT7-MED25 (bait) were grown on selective media lacking Ade, His, Leu, and Trp (SD/-4) to test protein interaction. ACID, activator-interacting domain; GD, glutamine-rich domain; LRR, leucine-rich repeat; MD, middle domain; PHD, plant homeodomain; vWF-A, von Willebrand factor A domain; Znf-TAZ, transcription adaptor putative Zinc finger (TAZ)-type Zinc finger; Znf-ZZ, two Zinc binding domain (ZZ)-type Zinc finger.