Fig. 1.
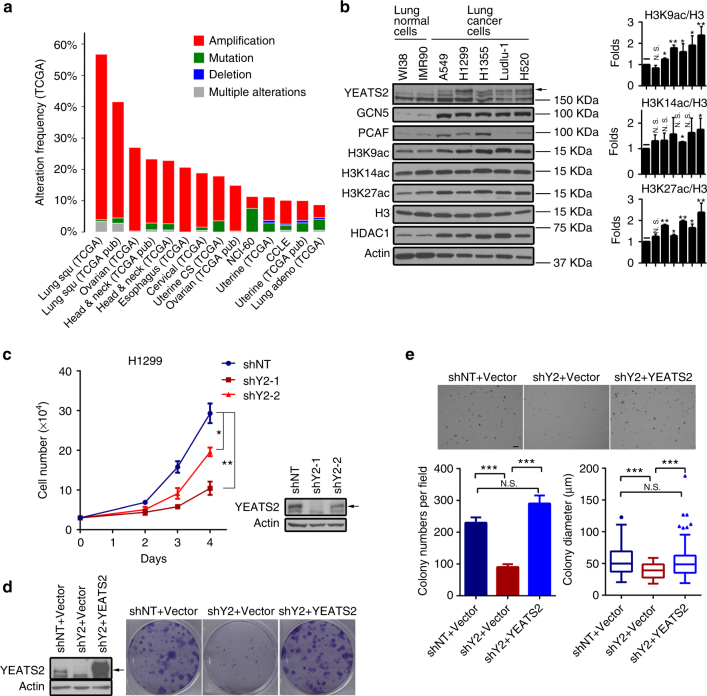
YEATS2 is amplified in NSCLC and is required for cancer cell growth and survival. a YEATS2 gene is frequently amplified in various types of human cancers. Data was obtained from the cBioPortal for Cancer Genomics. b Western blot analysis of YEATS2, GCN5, PCAF, HDAC1, and the indicated histone acetylation in NSCLC cell lines and immortalized “normal” lung fibroblast cell lines. Total H3 and actin are shown as loading control. The arrow indicates the band of YEATS2 protein. Relative H3K9ac, H3K14ac, and H3K27ac levels were quantified (n = 3, mean ± s.e.m.). N.S. not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). c Cell proliferation assay of H1299 cells treated with control (shNT) or YEATS2 shRNAs (shY2). Cells (mean ± S.E.M., n = 4) were counted for 4 days after seeding (left panel). Right panel: western blot analysis showing YEATS2 knockdown efficiency. The arrow indicates the band of YEATS2 protein. Error bars represent S.E.M. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). d Clonogenic assay of control (shNT), YEATS2 knockdown (shY2), and knockdown H1299 cells rescued with ectopic expression of YEATS2. Empty vector was used as a control. Colonies were stained and photographed 7 days after seeding (right panel). Left panel: western blot analysis of YEATS2 expression level in indicated cells. The arrow indicates the band of YEATS2 protein. e Anchorage-independent growth assay of H1299 cells as in (d). Cells (mean ± S.E.M., n = 4–6) were stained with 0.005% crystal violet blue and photographed 3 weeks after seeding (top panel). Colony numbers (bottom left) and colony diameters (bottom right) were measured and quantified using ImageJ software. Scale bar, 200 µm. N.S. not significant; ***p < 0.001 (Student’s t-test)