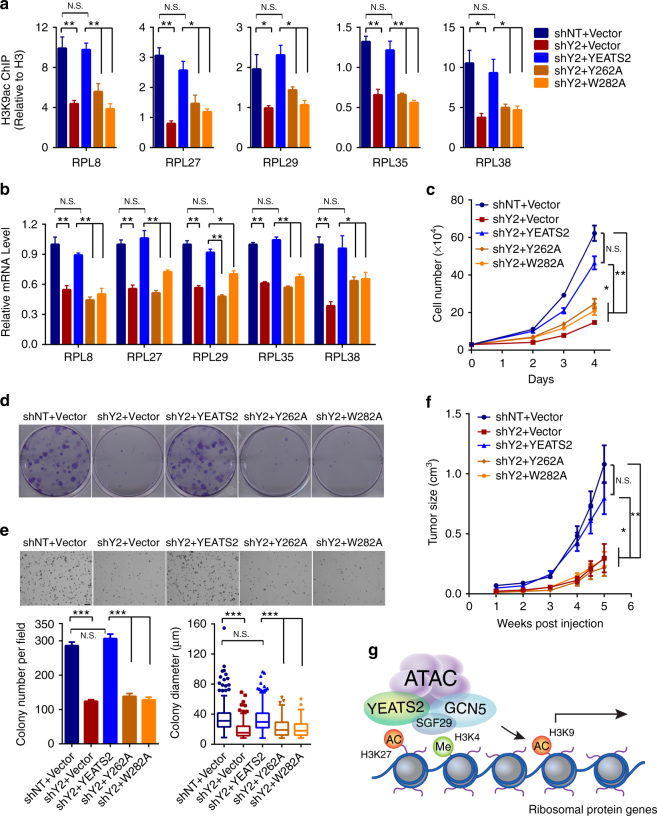
Fig. 6.
The YEATS domain of YEATS2 is required for ATAC-dependent ribosomal protein gene expression and tumor cell survival. a qPCR analysis of H3K9ac ChIP in the promoters of the indicated ribosomal protein genes in control (shNT) and YEATS2 KD (shY2) H1299 cells ectopically expressing shRNA-resistant WT YEATS2 or the indicated mutants. b qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of ribosomal protein genes in cells as in (a). In a and b, error bars indicate S.E.M. of at least three biological replicates. N.S. not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). c Cell proliferation assay of cells as in (a). Cells (mean ± S.E.M., n = 3) were counted for 4 days after seeding. Error bars represent the S.E.M. N.S.; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). d Clonogenic assay of cells as in (a). Colonies were stained and photographed 7 days after seeding. e Anchorage-independent growth assay of cells as in (a). Cells (mean ± S.E.M., n = 4–6) were stained and photographed 3 weeks after seeding. Colony numbers (bottom left) and diameters (bottom right) were measured using ImageJ software. Error bars represent the S.E.M. Scale bar, 200 µm. N.S.; ***p < 0.001 (Student’s t-test). f Volumes of tumors (mean ± S.E.M., n = 10) of the H1299 cells as in (a) subcutaneously transplanted into immunodeficient nude mice. Tumors were monitored for 5 weeks after transplantation. N.S.; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). g Working model: the YEATS2 subunit of the ATAC complex recognizes H3K27ac through its YEATS domain and stabilizes the ATAC complex at target promoter regions to maintain local histone acetylation and gene expression, which are essential for cell growth and survival. Note that additional reader modules, such as the SGF29 double Tudor domains that bind to H3K4me3, also contribute to chromatin association of the ATAC complex