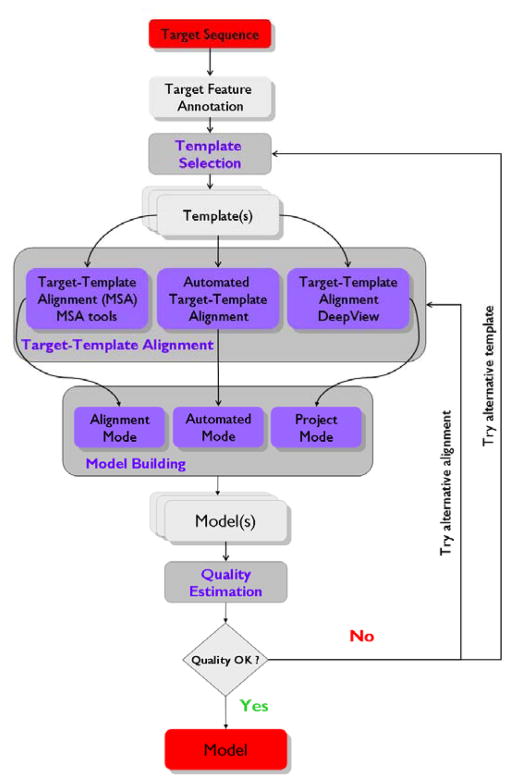
Fig. 1.
SWISS-MODEL workflow. The flowchart illustrates the classical steps to construct a homology model of a target sequence as they are implemented in SWISS-MODEL Workspace. Starting from the sequence of the protein of interest (target) one or more related structures (templates) are identified (template selection). Annotation of the target sequence (feature annotation) can guide the choice of appropriate template(s). Based on the evolutionary distance between target and template(s) sequences three different regimes of the target-template alignment step are available on the Swiss-Model Workspace: Automated, Alignment or Project Mode. Target and template(s) sequences are aligned (target-template alignment) either in a fully automated fashion, by using external alignment tools, and (optionally) adjusted visually with the help of the DeepView program. The model is then constructed based on these alignments. Finally the quality of the obtained model(s) can be estimated and verified and if necessary the procedure is repeated until a satisfactory result is obtained.