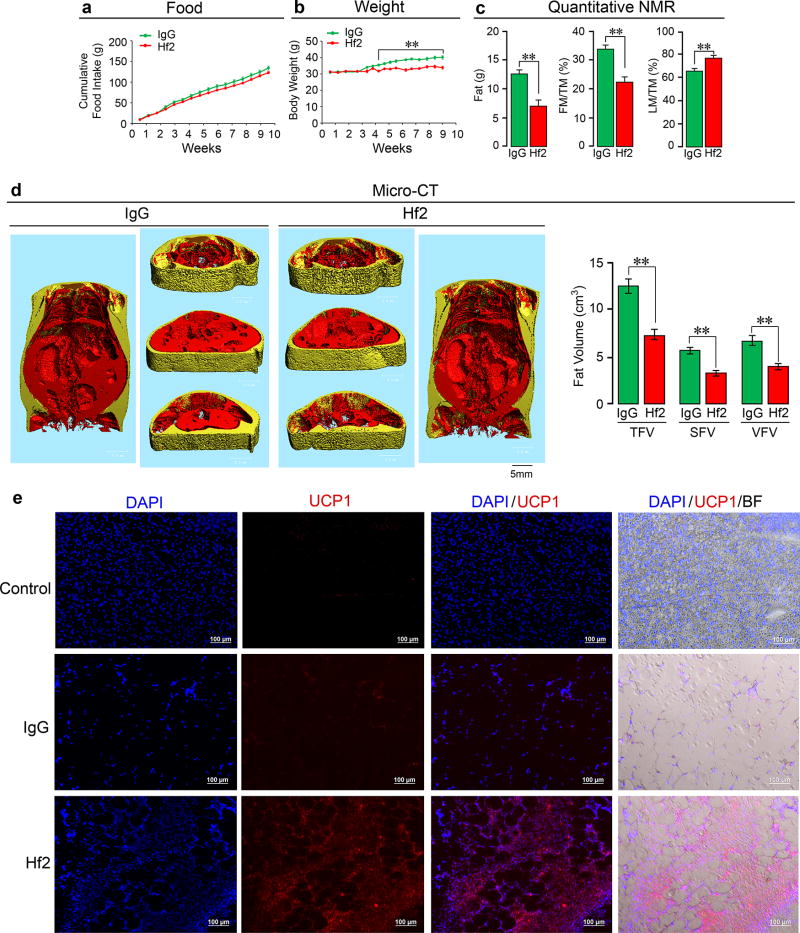
Extended Data Figure 9. Monoclonal Antibody Hf2 Against a Human FSHβ Epitope Markedly Reduces Body Weight and White Adipose Tissue and Induces Beiging in Mice Fed on a High-Fat Diet.
The monoclonal antibody Hf2 was raised against the 13-amino-acid-long human FSHβ sequence (LVYKDPARPKIQK), which corresponds to the mouse Fshβ sequence (LVYKDPARPNTQK) against which the polyclonal Ab was raised (please refer to Extended Data Fig. 1). Hf2 specifically binds human Fshβ in an ELISA. We have also sequenced Hf2 (data available on request). Shown is the effect of a ~9-week exposure to Hf2 or mouse IgG (200 µg/day/mouse, i.p.), injected daily into 6-month-old C57BL/6J mice pair-fed on high-fat diet (see Methods). Food intake (a), body weight (b), fat mass, fat mass/total mass (FM/TM) and lean mass/TM (LM/TM) (quantitative NMR) (c), and total (TFV), subcutaneous (SFV) and visceral (VFV) fat volume (micro-CT, coronal and transverse sections; visceral, red; subcutaneous, yellow) (d) are shown (n=5/group for a–d). Fluorescence and bright field micrographs showing Ucp1 immunostaining in frozen sections of visceral WAT (vWAT) (e). DAPI: nuclear staining. Negative control: irrelevant IgG in place of first antibody. There is a dramatic increase in Ucp1 immunostaining with Ab in vWAT, together with cell condensation, reminiscent of beiging. Statistics: Two-tailed Student’s t-Test, **P≤0.01; mean ± SEM. For body weight changes, please see Excel Spreadsheet. The proof-of-concept study shows that a profound anti-obesity action can result from targeting FSHβ with a monoclonal Ab, a prelude to translational efforts towards the future use of a humanized Hf2 or its equivalent in people.