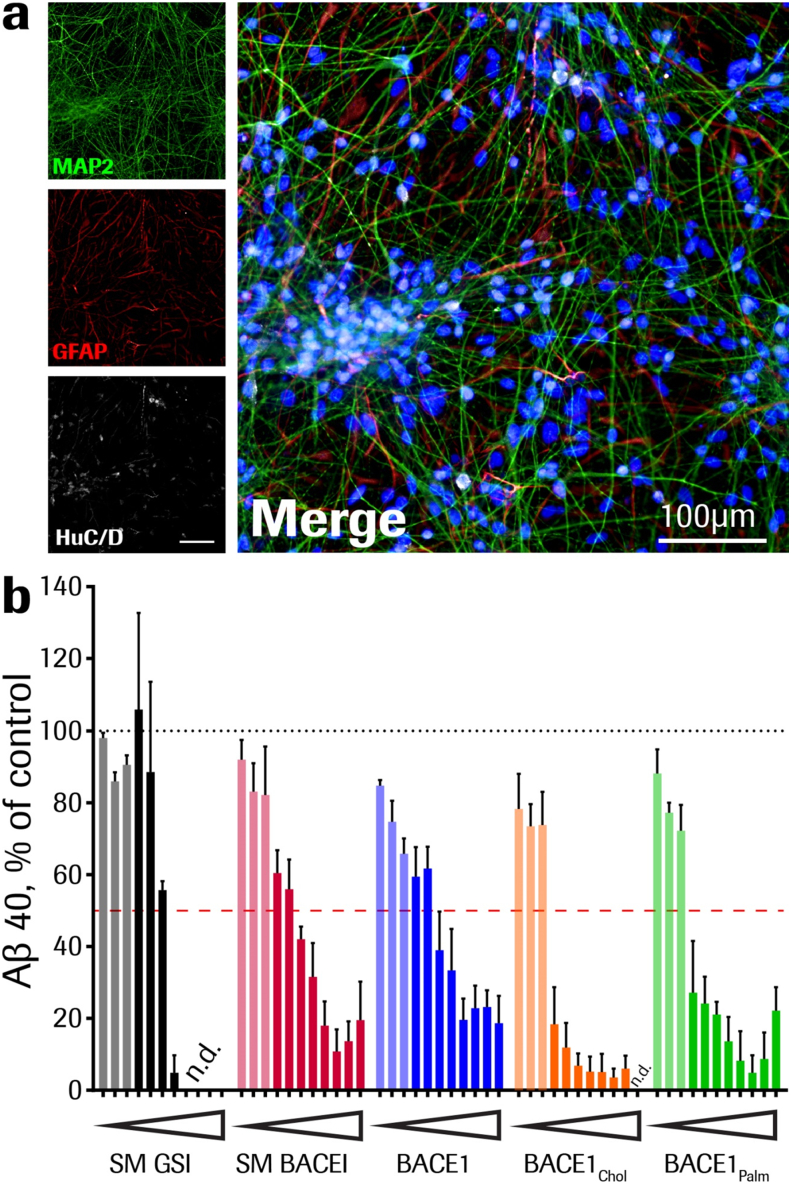
Fig. 5.
Aβ inhibition by BACE1 peptide inhibitors and small molecule β- and γ-secretase inhibitors in vitro. (a) Human stem-cell derived neurons were cultured for six weeks and neuronal identity verified by staining for markers like Map2 (green) and HuC/D (white). The level of astrocytes in fully differentiated cells was verified with anti-GFAP (red) labeling. As reference, cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). (b) Aβ production inhibition in human stem cell-derived neurons. Fully differentiated cells were incubated with the different compounds for 48 h at doses ranging from 10 to 0.001 μM, decreasing in half-logarithmic steps. Experimental setup included cells from three independent differentiations and two technical replicates each dose (0.128–10,000 nM; solid colors), and cells from one differentiation and two technical replicates each dose (0.001024–0.0256 nM; shaded colors). Both small molecule and BACE1 peptide inhibitors blocked Aβ production to a comparable extend, SM GSI (black bars), SM BACE1 (red bars), Pep#16 BACE1 (blue bars), Pep#15 BACE1palm (green bars) and Pep#14 BACE1chol (orange bars). All % values represent Aβ40 level changes in treated cells relative to respective vehicle-treated cells (means ± SEM). n.d. signal below detection limit.