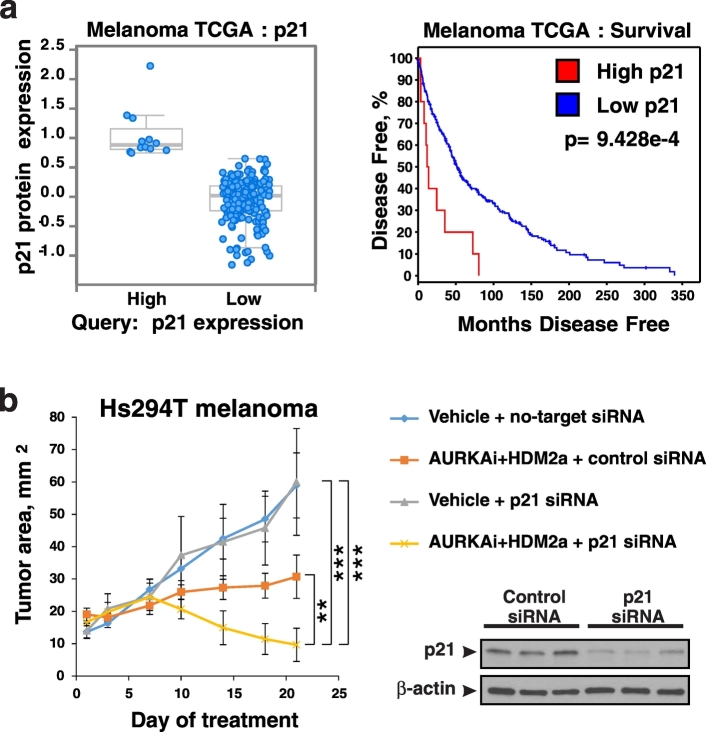
Fig. 7.
P21 as a potential therapeutic target in melanoma. (a) Analysis of the TCGA dataset of 479 melanoma specimens using cBio portal. Tumors were sorted into high and low expression of p21, based on p21 protein expression by RPPA analysis (left panel). Disease-free survival was compared between these groups (right panel). (b) Nude mice bearing Hs294T melanoma xenograft tumors were treated QD with 30 mg/kg alisertib (AURKAi) and 150 mg/kg idasanutlin (HDM2a). Animals also received injections of control siRNA (no-target siRNA) or p21 siRNA mixed with in vivo siRNA delivery reagent JetPei directly into the tumor twice a week. Tumor area (length x width) was measured every 3–4 days. Average tumor area ± SD is shown. N = 6 in vehicle groups and n = 7 in AURKAi and HDM2a treatment groups. Mixed-effects statistical model was used to assess group differences in tumor area over days. Expression of p21 in tumors from vehicle-treated mice injected with control or p21 siRNA was evaluated in whole tumor lysates by western blot with human p21-specific antibodies (right panel).