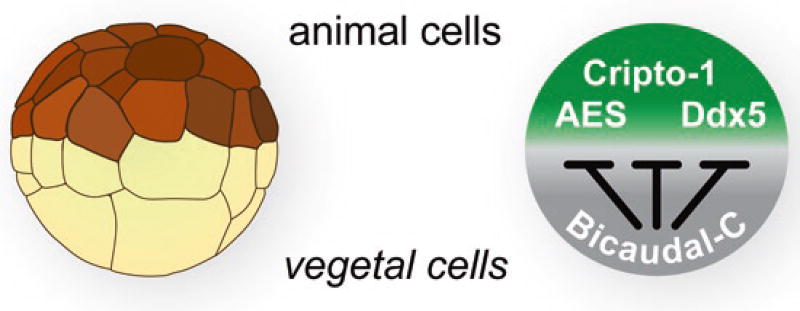
Fig. 2.6.
The Bic-C posttranscriptional network (Zhang et al. 2013). The vegetal cells of developing Xenopus embryos contain a high concentration of Bic-C that represses the translation of specific targets such as the AES, Cripto-1, and Ddx5 mRNAs. The protein products of Bic-C target mRNAs are potentially concentrated in animal cells due to their repression by Bic-C in vegetal cells