Figure 6. MIAT and DUSP7 shared a common miR-155-5p binding site.
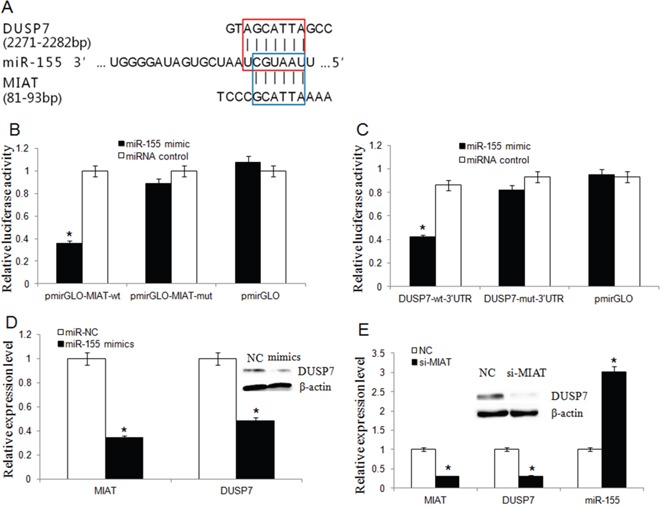
(A) Bioinformatics analysis revealed that MIAT and DUSP7 shared a common miR-155-5p binding site. The red box represented the binding site for miR-155-5p on the DUSP7 mRNA 3′-UTR, and the blue box represented the binding site for miR-155-5p on MIAT. (B) Luciferase activity in HEK293T cells cotransfected with miR-155-5p mimics and luciferase reporters containing control vector, pmir-Glo-MIAT-wt and pmir-Glo-MIAT-mut (*P<0.05, Two-side Student's t-test; n = 3). miR-155-5p mimics reduced the luciferase activity of wt MIAT reporter vector but not that of mut MIAT reporter vector. (C) MiR-155-5p significantly inhibited the luciferase activity of the DUSP7 wt 3′-UTR but not that of the mutant (*P <0.05, Two-side Student's t-test; n = 3). (D) MiR-155-5p overexpression downregulated the endogenic MIAT and DUSP7 expression. (*P <0.05, Two-side Student's t-test; n = 3). Western blot assay showed that miR-155-5p overexpression silenced DUSP7 protein expression. (E) The miR-155-5p level was increased but DUSP7 mRNA level was decreased in MDA-MB-231 cells after MIAT knockdown. (Data are presented as mean ± SD, n=3. *P <0.05). Western blot assay showed that knockdown of MIAT triggered a significant silencing effect on endogenous DUSP7 protein.
