Figure 4. Compound 14 inhibits cell viability and increases apoptosis in vitro and in vivo.
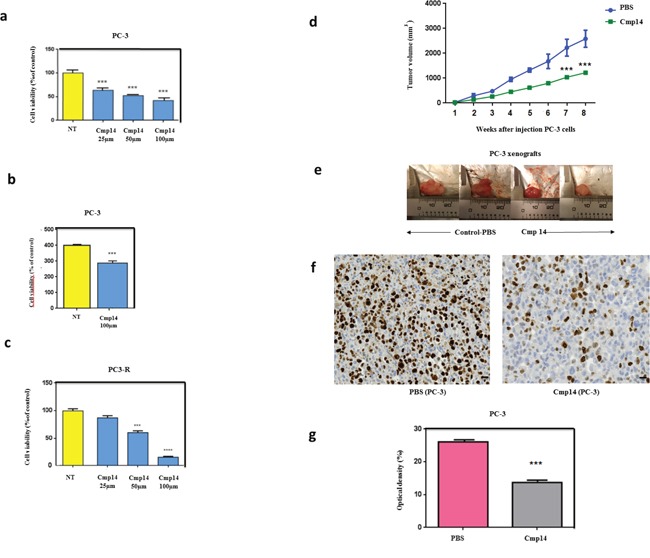
Cells viability using MTT assay (a) was performed on PC-3 non treated (NT) or treated cells with compound 14 (a) at different concentrations (25, 50, 100μM) during 48h. Cell death quantification (SubG0 phase) using flow cytometry (b) was performed on PC-3 cells non treated (NT) or treated with compound 14 at 100μM during 48h. Cell viability using MTT assay was also performed on PC-3-docetaxel resistant cells non treated (NT) or treated with compound 14 (c) at different concentrations (25, 50, 100μM) during 48h. (d) PC-3 cells were subcutaneously implanted in Node Scids by injection of 10 ×10 6 cells in the right flank of animals. When tumors reached 100mm3, mice were randomized in two groups that received twice a week an intra-peritoneal injection of PBS (control n = 6, blue) and phenazine 14 (n = 8, green) (1 mg/kg) for 8 weeks. Tumor volume was measured once weekly and calculated by the formula length x width x depth x 0.5236. Compound 14 reduced significantly PC-3 tumor volume by up to 50%. During the entire treatment period, all mice treated with PBS and 14 did not show any abnormal behavior, and no significant alteration of mice body weight was observed. (e) Photographs of PC-3 harvested tumors from mice that received i.p. compound 14 or control-PBS after an 8-week treatment (f) Ki-67 IHC staining of tumor tissues to assess tumor cells proliferation. (g) Distribution of tissue Ki-67 immunostaining intensity (measured as average optical density) according to the tumor treated with PBS and Compoud#14. Error bars represent the SE, **, P ≤0.01 and ***, P ≤ 0.001 by Statview software.
