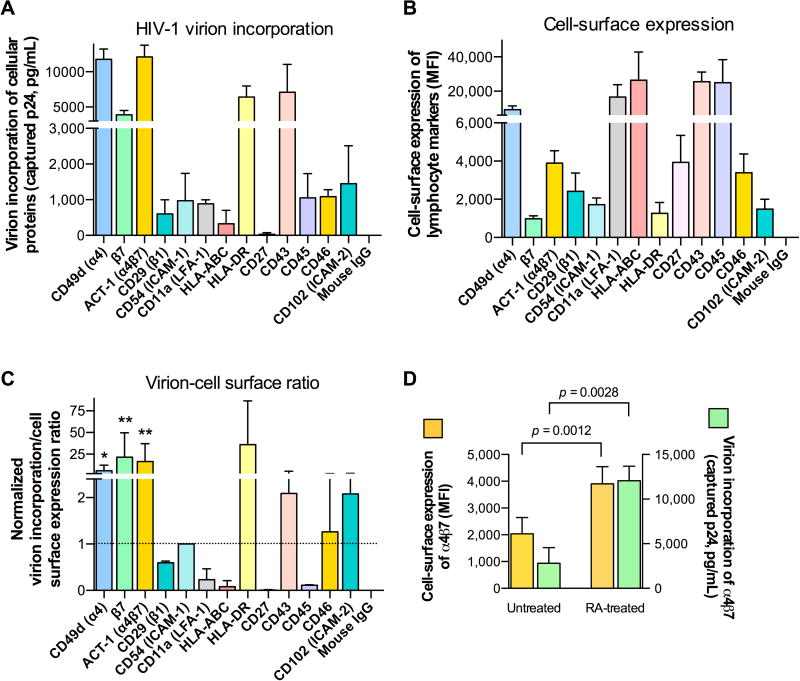
Fig. 1. HIV-1 virions efficiently incorporate integrin α4β7.
(A) Immunomagnetic capture of virion progeny (HIV-1 SF162) produced by RA-activated human PBMC cells using mAbs directed against a panel of cell surface-expressed lymphocyte antigens. Captured virions from identical viral inputs were quantified for p24Gag antigen concentrations by AlphaLisa. The data represent the mean (±SD) of three biological replicates performed using PBMC from three different healthy blood donors. (B) Cell-surface staining of HIV-infected RA-activated human PBMC using the same panel of mAbs as in panel A. Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) values obtained with normalized antibody concentrations are shown. The data represent the mean (±SD) of three biological replicates performed using virus produced by PBMC from three different healthy blood donors. (C) Ratio between virion incorporation and cell-surface expression for each lymphocyte marker, with the calculated ratio for ICAM-1 set at 1, as a reference. To obtain an index of incorporation efficiency, we first normalized the levels of both virion incorporation and cell-surface expression to the respective levels detected with ICAM-1, selected as a reference protein; then, for each protein we calculated the ratio between normalized virion incorporation and normalized cell-surface expression. The incorporation of integrin α4β7 (mAb ACT-1) was significantly higher than that of ICAM-1. * p = 0.025; ** p < 0.01 by paired two-tailed t-test. (D) Parallel analysis of α4β7 cell-surface expression (yellow bars, left y-axis) and virion incorporation (green bars, right y-axis) in cultures of RA-treated and untreated human PBMC infected with HIV-1 SF162. The data represent the mean (±SD) of three biological replicates performed using PBMC and respective progeny virus from three different healthy blood donors.