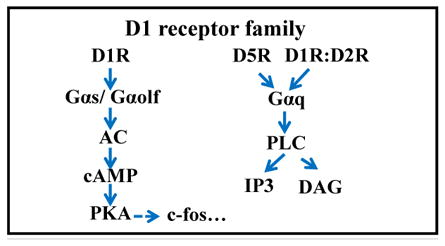
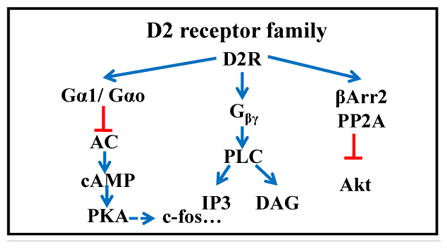
Table 1. Dopamine receptor biology in retina: signaling, distribution and pharmacology.
The two main families of dopamine receptors are listed with their receptor subtypes and various agonists and antagonists. RP: photoreceptor; BC: bipolar cell; HC: horizontal cell; AC: amacrine cell; RGC: retinal ganglion cell; RPE: retinal pigment epithelium.
|
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||
| D1 | D5 | D2 | D3 | D4 | ||
|
| ||||||
| Retinal distribution | Type-specific BCs, HCs, a set of ACs, RGCs | RPE | PR Dopaminergic ACs | none | PR (mouse) | |
| Agonist Ki value (nM) | Dopamine | 0.9–2340 | <0.9–261 | 2.8–474 | 4–27 | 28–450 |
| Apomorphine | 0.7–680 | 122–168 | 0.7–24 | 20–32 | 4 | |
| ADTN | 2.9–>10000 | n/a | 1–1370 | n/a | 393 | |
| SKF-38393 | 1–150 | 0.5–100 | 150-9560 | 5000 | 1000–1300 | |
| PD-168077 | >10000 | n/a | 2820-3740 | 2810 | 8.7–25 | |
| Antagonist Ki value (nM) | Haloperidol | 27–203 | 33-151 | 0.6–1.2 | 2.74-7.8 | 2.3–5.1 |
| Spiperone | 99–350 | 135-4500 | 0.06–0.37 | 0.32–0.71 | 0.05–4 | |
| SCH-23390 | 0.11–0.35 | 0.11-0.54 | 270–1100 | 314–800 | 3000–3560 | |
| Sulpiride | 20400–45000 | 11000–77270 | 2.5–7.1 | 8–206 | 21–1000 | |
| L-745870 | n/a | n/a | 960 | 2300 | 0.43 | |
| Methylergonovine | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a | |
