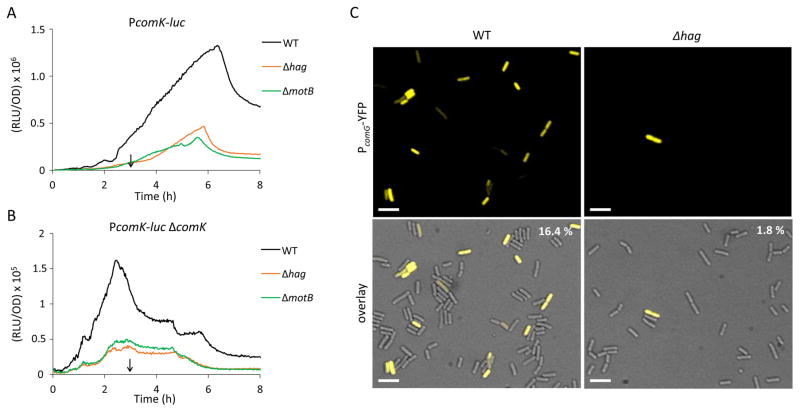
Figure 2.
Deletion of hag and motB lower the expression of comK and a Δhag mutation lowers the frequency of entry to the K-state. The effects of hag and motB knockouts on PcomK-luc expression in the presence (A) or absence (B) of ComK are shown. The following strains were used in these experiments: wild-type PcomK-luc (BD4773), Δhag PcomK-luc (BD7636), ΔmotB PcomK-luc (BD7466), ΔcomK PcomK-luc (BD4893), Δhag ΔcomK PcomK-luc (BD7261) and ΔmotB ΔcomK PcomK-luc (BD7488). The expression profiles in A and B are plotted on different scales. The vertical arrows in panels A and B point to T0. (C) Single-cell expression and microscopic enumeration of PcomG-yfp expressing cells in Δhag (BD7262) and wild-type (BD5783) populations. The indicated strains were grown to the time of maximum K-state expression (T2) and samples were taken for microscopy. Representative images are shown. In the upper right corner are the average percentages of K-state cells determined by counting at least 1000 cells for each strain, done in duplicate. Scale bar is 5μm.