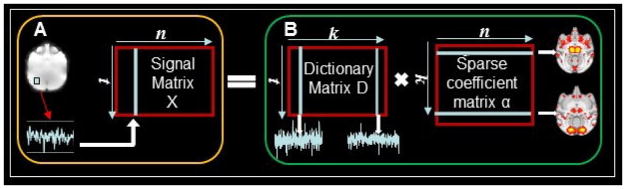
Fig. 2.
The computational framework of identification of connectome-scale ICNs in each individual subject via dictionary learning and sparse representation of whole-brain rsfMRI signals. (a) The aggregated signal matrix X based on whole-brain rsfMRI signals of one subject. n is the number of voxels within the whole-brain and t is the rsfMRI time points. (b) The learned dictionary matrix D and sparse coefficient matrix α via sparse representation of X. Each column of D is a dictionary atom representing the temporal pattern of a ICN and corresponding row of α can be mapped back to brain volume to obtain the spatial pattern of the ICN. Each element of α is the functional activity value. k is the dictionary atom number.