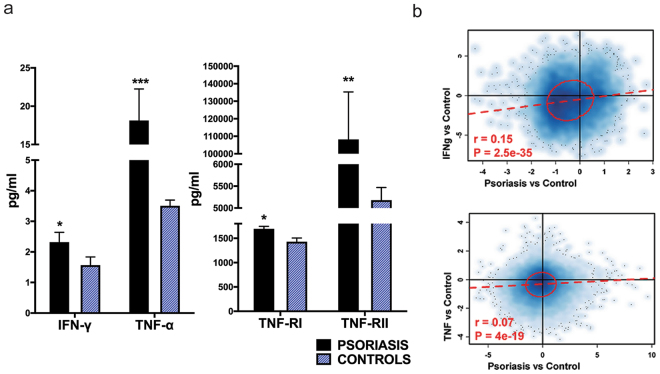
Figure 3.
Serum IFN-γ and TNF is increased in psoriasis compared to healthy controls. (a) Serum IFN-γ was approximately 2.4-fold higher in patients with psoriasis compared to healthy controls, whereas serum TNF-α was about 31-fold higher (n = 112 patients, n = 54 controls, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, Student’s t-tests). Serum levels of TNFRI and TNFR-II were 1.2-fold and 21-fold higher respectively in patients with psoriasis compared to controls (n = 120 patients, n = 29 controls, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, Student’s t-tests). (b) Global gene expression from PBMCs from psoriasis patients vs. control (n = 5 psoriasis vs. n = 5 controls) compared against data obtained from TNF and IFN-γ stimulated vs. unstimulated PBMCs, demonstrates positive correlation with IFN-γ and TNF-α responses (p = 2.5 × 10−35, p = 4 × 10−19 respectively, Spearman rank correlation). Data are shown as mean ± SEM with 95% CI.