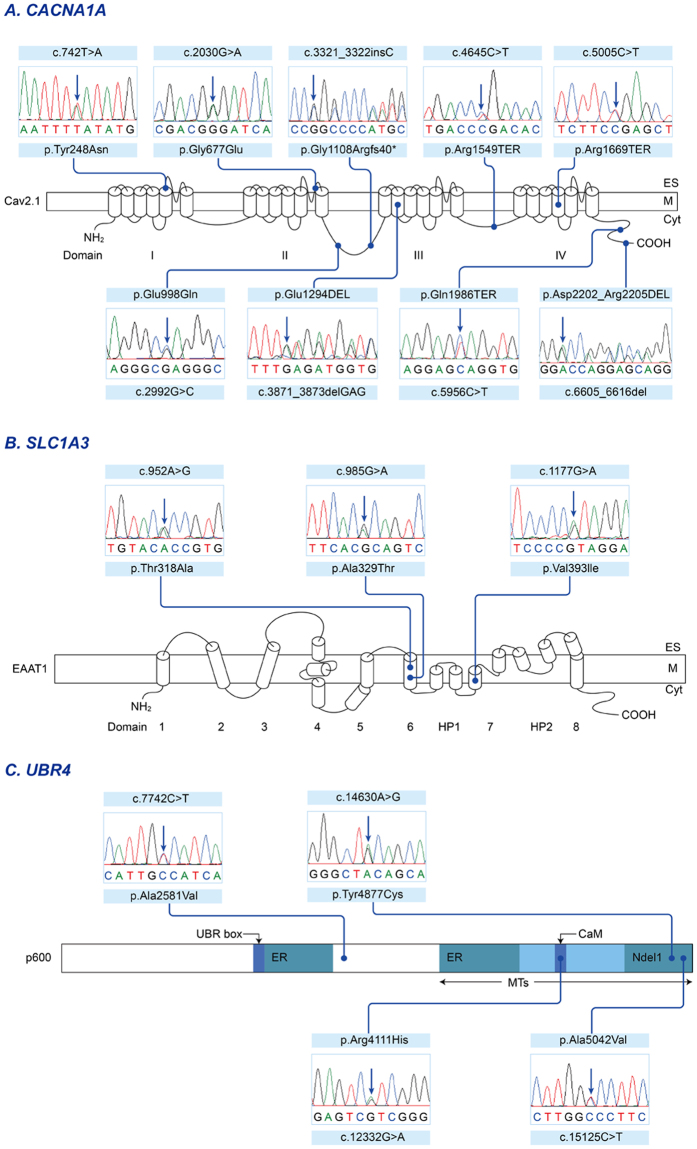
Figure 2.
Sequencing results and localization of the mutations in EA genes. (A) The Cav2.1 encoded by CACNA1A has four homologous domains (I-IV), each consisting of six transmembrane segments (S1-S6) and an additional pore loop located between S5 and S6. Three non-sense mutations (p.Arg1549TER of patient 16, p.Arg1669TER of patient 5 and p.Gln1986TER of patient 2) are predicted premature termination in the S4 of Domain IV or the C-terminal domain. A heterozygous insertion mutation is located in the intracellular linker connecting Domain II and III, and lead to a frameshift and premature termination (p.Gly1108Argfs40TER of patient 15). Two missense mutations (p.Gly677Glu of patient 1 and p.Tyr248Asn of patient 4) involve the pore region (S5-S6) of Domain II and I, respectively. The other missense mutation (p.Glu998Gln of patient 5) is located in the intracellular linker. The in-frame deletions without truncation of the protein (p.Glu1294DEL of patient 3 and p.Asp2202_Arg2205DEL of patient 15) are in the S2 of Domain III and the C-terminal domain, respectively. (B) The EAAT1 encoded by SLC1A3 is composed of eight alpha-helical transmembrane domains (TMDs) and re-entrant hairpin loops (HP) 1 and 2 flanking TMD7. The first sixth TMDs form a scaffold that surrounds a C-terminal core domain comprising HP1, TMD7, HP2, and TMD8. Two missense mutations (p.Ala329Thr of patient 3 and p.Thr318Ala of patient 23) are located in TMD6, while the other mutation (p.Val393Ile of patient 6) is located in TMD7, the critical binding site for glutamate and various coupled ions, Na+, H+ and K+. (C) The p600 protein encoded by UBR4 contains several identified functional domains including UBR box, microtubule (MT)-binding domains, and calmodulin (CaM)-binding domain. The two endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-binding regions are located near the center of the protein and within the MT-binding domain. The Ndel1-binding region overlaps with the MT-binding domain. Three missense mutations (p.Arg4111His of patient 5, p.Tyr4877Cys of patient 2, and p.Ala5042Val of patient 26) are located within the MT-binding domain, and one (p.Arg4111His) involves the CaM-binding domain interacting with calmodulin. The other one (p.Ala2581Val of patient 28) is situated in the functionally-unknown region.