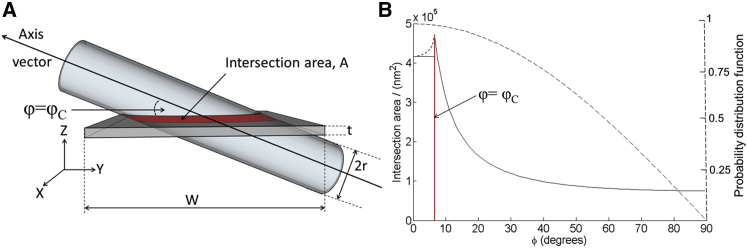
Figure 9.
(A) Model of the intersection area, A, of a cylindrical structure (T-tub) of radius r and a slab (TEM image section) of width W and thickness t. The cylinder axis makes an angle φ with the plane of the slab and the cylinder is shown oriented at the critical angle (φ = φC). (B) The solid line describes the variation in the interface area, A (left axis), as a function of the inclination angle of the cylinder, φ, as predicted by the model. The small-dashed black line predicts the variation in intersection area for φ < φC. The large-dashed line indicates the probability distribution function (right axis) for the cylinder orientation as a function of φ.