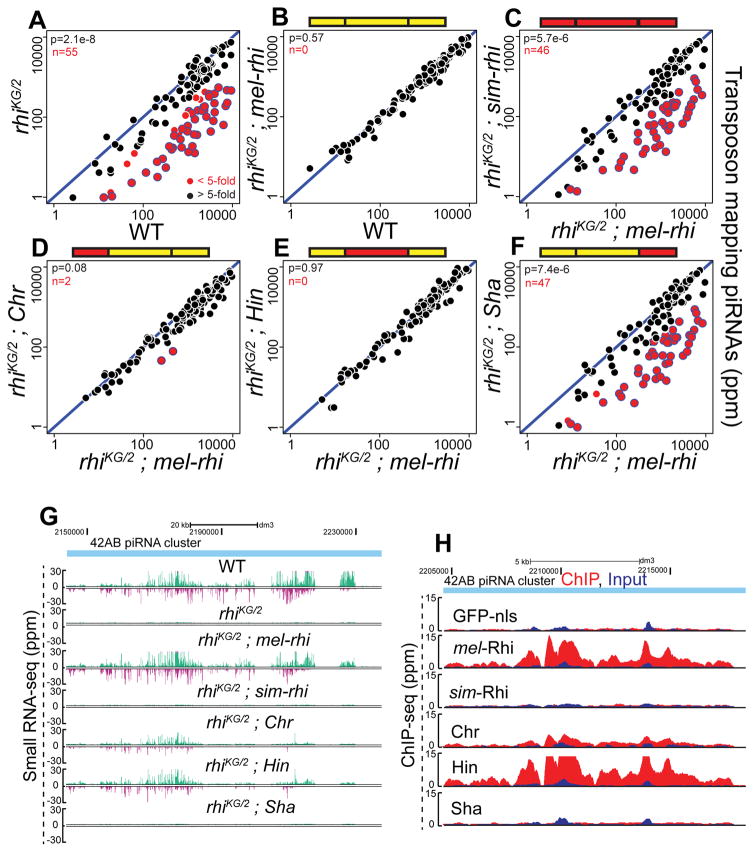
Figure 3. sim-Rhi and Shadow chimera do not bind to piRNA clusters and fail to support piRNA production.
(A–F) Scatterplots showing abundance of transposon mapping piRNAs in ovaries of rhi mutant (A), rhi mutant expressing either mel-rhi (B) vs. WT control, sim-rhi (C) or the chimeras (D-F) vs. mel-rhi. Points in red show x/y>5 (n is number of these transposons). Blue bordered points have reduced expression in rhi mutants, rhi mutants expressing sim-Rhi, and rhi mutants expressing the Sha chimera. p value for differences is obtained by Wilcoxon test.
(G) Genome browser view showing abundance of piRNAs uniquely mapping to 42AB piRNA cluster in WT, rhi mutant and rhi mutants expressing mel-rhi, sim-rhi or chimeric proteins. The Watson strand is in green, and Crick strand in magenta.
(H) Genome browser view of ChIP-seq profiles at 42AB cluster for mel-Rhi, sim-Rhi, chimeras, and GFP-nls control. All ChIP done under identical conditions, using the same anti-GFP antibody. ChIP signal in red, input signal in blue.
See also Figure S3.