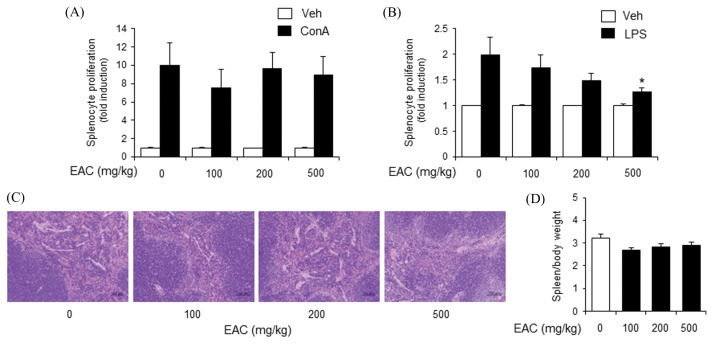
Fig. 4.
Oral administration of Artemisia capillaris ethanol extract decreases LPS-induced primary mouse splenocyte proliferation. Balb/c mice were orally administered an ethanol extract (EAC) of A. capillaris. (A), (B). After 24 hr, splenocytes were isolated and stimulated with concanavalin A (ConA; 5 μg/mL) or lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 10 μg/mL). Cellular proliferation was measured by methylthiazol tetrazolium (MTT) assay. (C) Spleens were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. (D) Spleen weight per body weight. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3). *Significantly different from ConA or LPS alone, p < 0.05. Veh, vehicle.