Figure 4. Similarity in the Fibrinolytic Potential of humans and rabbits with empyema.
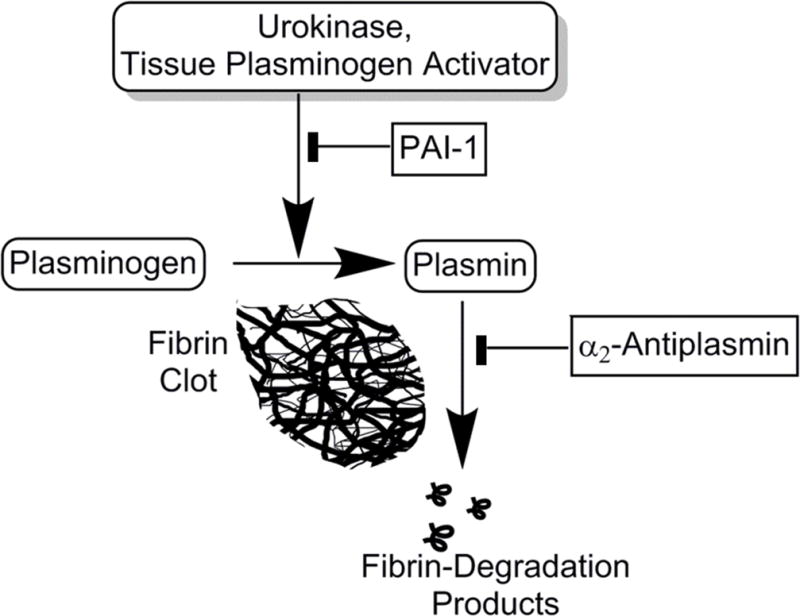
A semi-logarithmic plot of changes in the fibrinolytic activity in pleural fluids of rabbits and humans with infectious pleural injury is illustrated. Low level baseline fibrinolytic activity (FA0) reflects inhibition of plasminogen activation that are characteristically observed in baseline empyema fluid samples. Supplementation of pleural fluid with exogenous plasminogen activator (4 nM uPA) inhibits PAI-1, activates accumulated plasminogen and results in a considerable (up to 3 orders of magnitude) increase in the level of the fibrinolytic activity (FAuPA). Notably, the Fibrinolytic Potential (FP= FAuPA – FAo; baseline) varies significantly among animals and among humans. While two chain uPA was used in this example, any fibrinolysin can be used in this assay.
