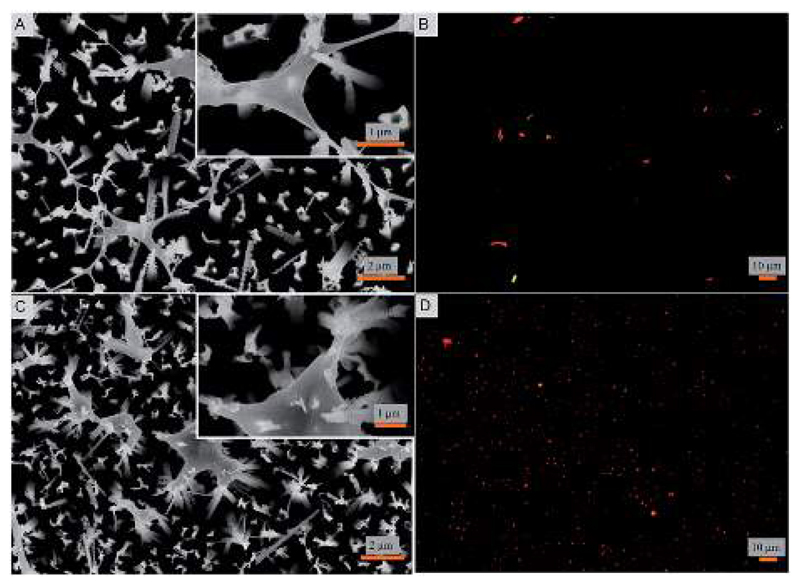
Fig. 2.
(A and C) Scanning electron micrographs and (B and D) fluorescent microscopic images of bacterial attachment on the fabricated super surfaces. E. coli (A and B) and S. aureus (C and D) cells are shown to be ruptured by the nanopillars. The fluorescent micrographs display the viable (green) and non-viable (red) cells.