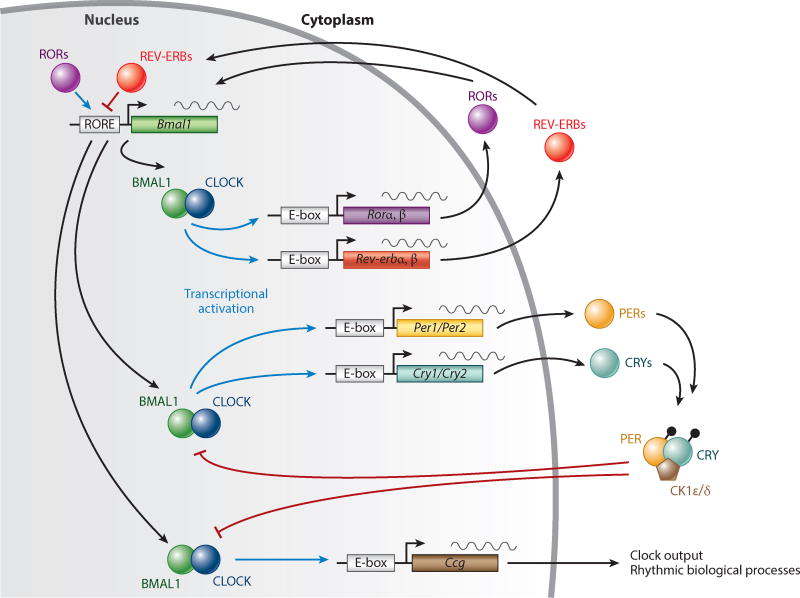
Figure 1.
The molecular clock in every cell consists of reciprocal positive and negative feedback loops. CLOCK and BMAL1 form heterodimers that activate the transcription of Cry and Per genes. PER dimerizes with CRY to inhibit CLOCK-BMAL1–mediated transcription. The timing of dimerization, complex formation, and translocation into the nucleus determines the cellular rhythms. Abbreviations: Ccg, clock controlled gene; CK1ε/δ, casein kinase 1ε/δ; CRY, cryptochrome; E-box, enhancer-box; PER, period; ROR, retinoic acid–related orphan receptor; RORE, RevDR2 and ROR-binding element. Figure adapted from Takahashi (2017).