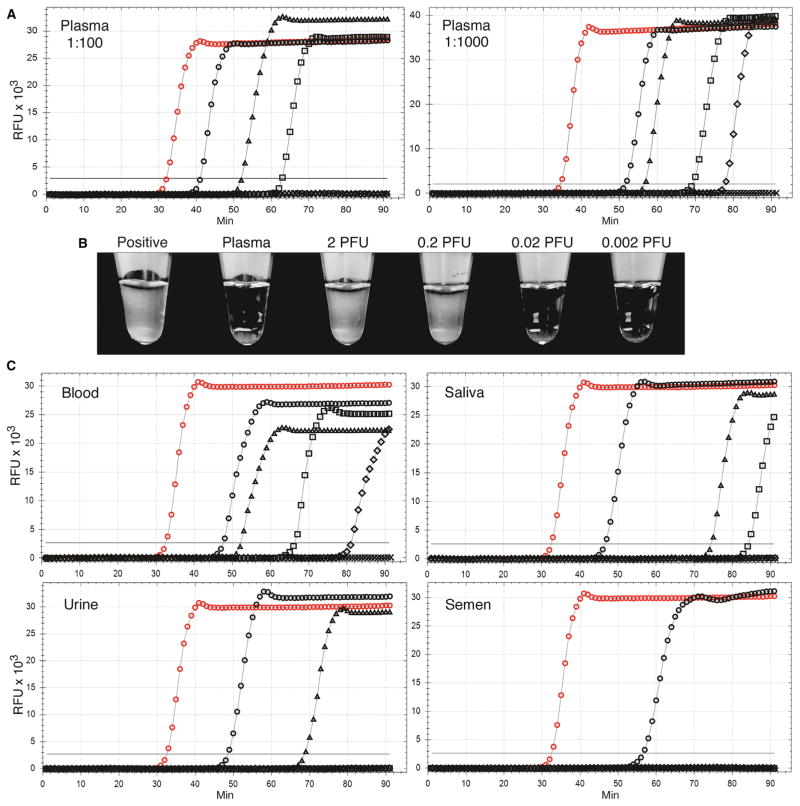
Fig. 5. Detection of Zika virus spiked into human blood, plasma, saliva, urine, and semen samples.
Healthy human biofluids were spiked with the Zika virus PRVABC59 strain from infected Vero cell supernatants at a final concentration of 106 PFU/ml. (A) Amplification of 2 μl of serial 10-fold dilutions of plasma containing 106 PFU/ml of the PRVABC59 strain followed by dilution to 1:100 or 1:1000 in water. (B) Matching samples of the 1:1000 plasma dilutions were incubated in tubes in a heat block for 70 min and examined for turbidity. (C) Tenfold dilutions of blood, saliva, urine, and semen each spiked with 106 PFU/ml of PRVABC59 Zika virus strain followed by dilution to 1:1000 in water. Virus input: (A and C) 2000 PFU (black circles), 200 PFU (black triangles), 20 PFU (black squares), 2 PFU (black diamonds), 0.2 PFU (black crosses; below threshold), 0.02 PFU (no symbols; gray line below threshold), infected Vero cell RNA (positive control; red circles), and diluted biofluids without virus (no symbols; black line below threshold). Results are representative of a minimum of six replicates of each dilution series. X axis, minutes to LAMP amplicon incorporation of fluorescent dye; y axis, RFUs.