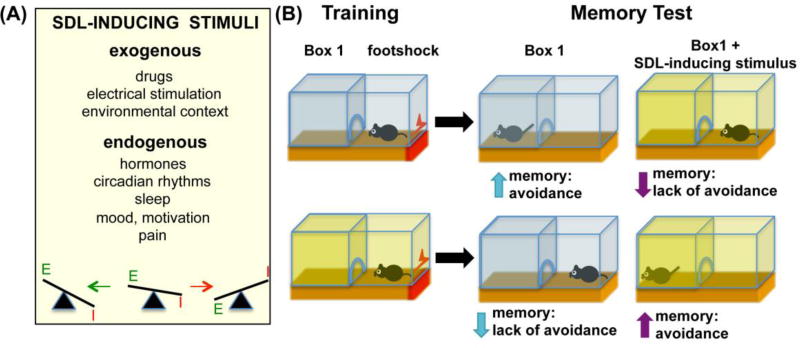
Figure 1.
Inducing SDL by stimuli that change the excitatory/inhibitory balance. (A) Exogenous and endogenous stimuli known to induce SDL. (B) SDL in an example of a passive avoidance paradigm, where the presence of memory is reflected by avoidance of the shock compartment at test. Top, memories learned under normal conditions are easily retrieved under similar conditions, but not if SDL-inducing stimuli are applied before the test. Bottom, memories learnt under SDL-inducing stimuli are not accessible for retrieval under normal conditions but can be retrieved if the same stimuli are reapplied. E, excitation; I, inhibition.