Figure 1.
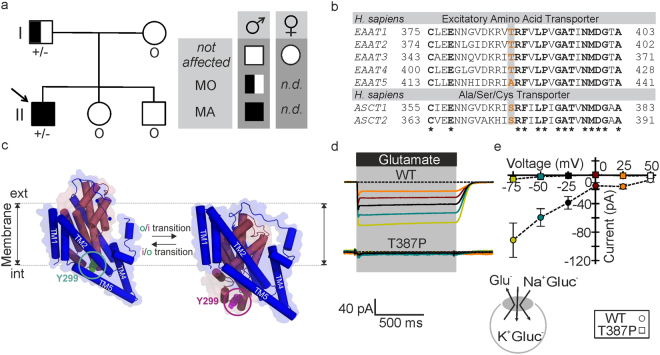
SLC1A3 mutation causes the exchange of the conserved threonine 387 by proline in hEAAT1. (a) Pedigree of the kindred with SLC1A3 T387P mutation. MA: migraine with aura (including hemiplegia); MO: migraine without aura. Arrow: index patient. Genotypes are indicated below each symbol (+/− denotes heterozygosity for SLC1A3 T387P variant; o DNA not available). (b) On the protein level, the variant causes a threonine (ACC) to proline (CCC) change at position 387. Multiple alignment of human excitatory amino acid transporters (hEAATs) and neutral amino acid transporters (ASCTs) shows that the T387 homologue positions in the transporter isoforms are preferentially occupied by hydroxylated amino acids. (c) Position of the T387- homologue residue Y299 in the EAAT topology model in the outward (o, green circle, modified from 2NWX.pdb) and inward (i, magenta circle, modified from 4P3J.pdb) conformation (dark purple: trimerization domain; dark red: transport domain). (d) Representative current traces from whole-cell patch clamp recordings from HEK293T cells expressing WT (top) and T387P (bottom) hEAAT1 under uptake conditions with permeant anions substituted by gluconate. Pipette solution (in mM): 115 K-gluc, 2 Mg-gluc, 5 EGTA, pH 7.4; Bath solution: 140 K-gluc, 1 Mg-gluc, 2 Ca-gluc, 5 TEA, pH 7.4, ± 5 L-Glutamate. Glutamate perfusion is indicated by a horizontal black bar. (e) Current-voltage relationship from glutamate transport for WT (circles) and mutant (squares, n = 5/5) hEAAT1. Holding potentials used in the transport experiments are color-coded.