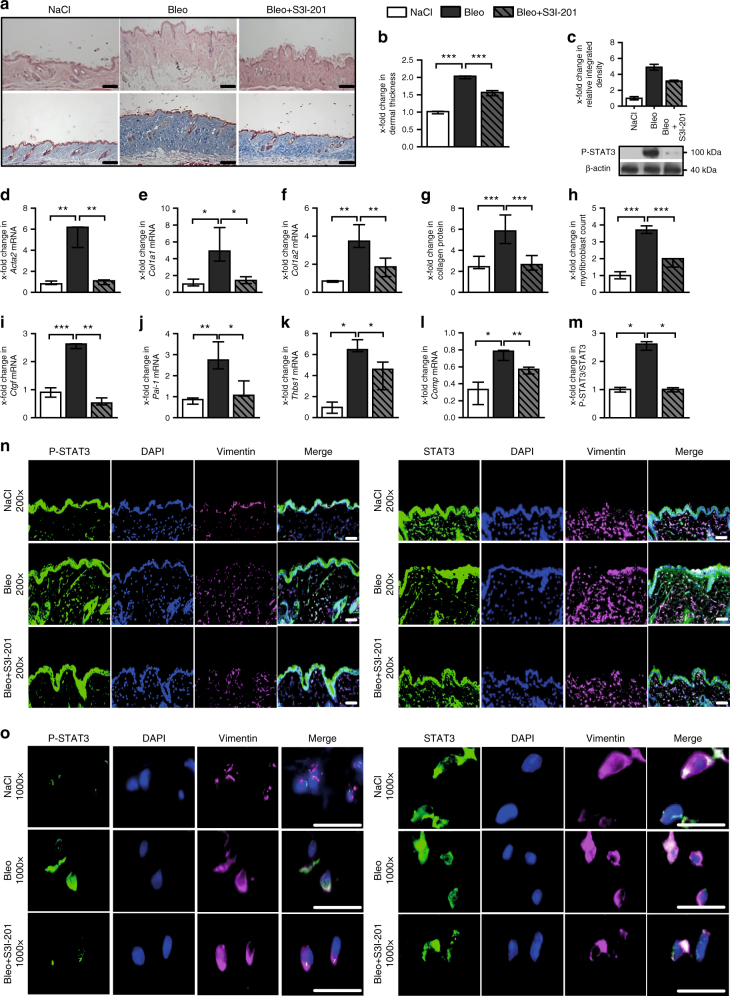
Fig. 10.
Pharmacological inhibition of STAT3 exerts potent anti-fibrotic effects in bleomycin-induced experimental skin fibrosis model. a–o Treatment of bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis with the STAT3 inhibitor S3I-201 in mice (DBA/2 background, 12 weeks of age). a Representative histological sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin (top) and trichrome (bottom). b Dermal thickness, c western blot analysis of P-STAT3, shown by the ladder representing 100 kDa (expected intense upper band size, 86 kDa and lower faint band size, 79 kDa). Beta-actin (expected molecular weight/size, 42 kDa) is shown by ladder at 40 kDa. d–f mRNA levels of d Acta2, e Col1a1, and f Col1a2, g hydroxyproline content, h myofibroblast counts and levels of i Ctgf mRNA, j Pai-1 mRNA and of the proposed biomarkers, k Thbs1 mRNA, and l Comp mRNA. m–o Immunofluorescence analysis including n, o representative immmunofluorescence stainings of P-STAT3 (left) and total STAT3 (right) at 200-fold and 1000-fold magnification, respectively, along with their m quantitative analyses. N ≥ 6 mice with 2 technical replicates per group for all experiments. Results are shown as median ± interquartile range (IQR). Horizontal scale bar, 100 μm. Significance was determined by Mann–Whitney test, as compared to vehicle-treated, fibrotic mice, respectively. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01***; P < 0.001