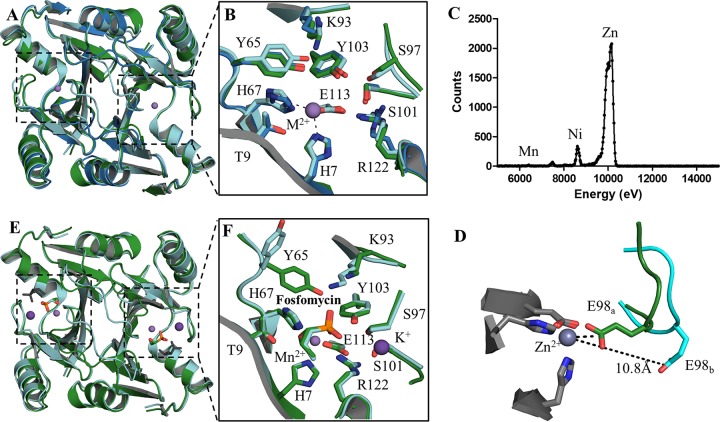
FIG 3.
Three-dimensional structures of the apo and holo forms of FosAKP and FosA3. (A) Overlay of the apo forms of FosAPA (red), FosA3 (blue), and FosAKP (green). (B) Active-site residues in the apo forms of FosA with residues labeled using FosAKP numbering. (C) Excitation scan of Zn-K edge in apo FosAKP crystal. (D) E98, which sits on the K+-binding loop, exhibits two conformations in apo FosAKP. (E) Superimposition of holo forms of FosAPA (cyan) and FosAKP (green) with a second nonphysiological fosfomycin (gray) bound in the FosAPA structure. (F) The holo active site is highly conserved with the exception of Y65, which adopts a different rotamer in FosAPA, likely due to a contact with a second fosfomycin molecule (not shown).