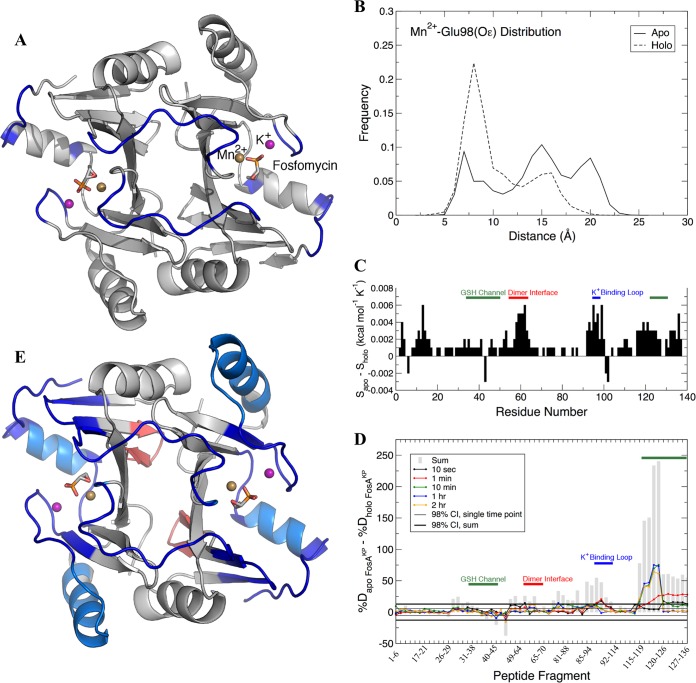
FIG 5.
Dynamic analysis of FosAKP from MD (A to C) and HDX-MS (D and E). (A) Regions of FosAKP that showed the greatest differences in dynamics between the apo and holo forms. The protein dimer is rendered in gray, with residues identified by DIRECT-ID to undergo changes in their dynamics in blue. The bound Mn2+ ion (gold), K+ ion (purple), and fosfomycin (stick) are shown for perspective. (B) Distance distributions between E98 Oε atoms and Mn2+ for apo and holo forms. (C) Per-residue entropy differences between the apo and holo forms of FosAKP with glutathione (GSH) channel, dimer interface, and K+-binding loop residues highlighted. (D) Fosfomycin-induced changes in hydrogen-deuterium exchange of FosAKP, with peptides that contain residues from the GSH channel, dimer interface, and K+-binding loop highlighted. Differences in deuteration between peptides from apo and holo FosAKP at individual time points are plotted as colored lines, with the sum of the differences over all time points plotted as gray bars. Confidence intervals (98%) for individual time points and sums are plotted as thin and thick black lines, respectively. (E) Cartoon representation of fosfomycin-induced changes in hydrogen-deuterium exchange of FosAKP. Regions with statistically significant decreases in deuteration at the earliest time point (10 s) are colored dark blue. Regions with decreases in deuteration observed only at later time points are colored light blue. Regions with increased deuteration are colored red.