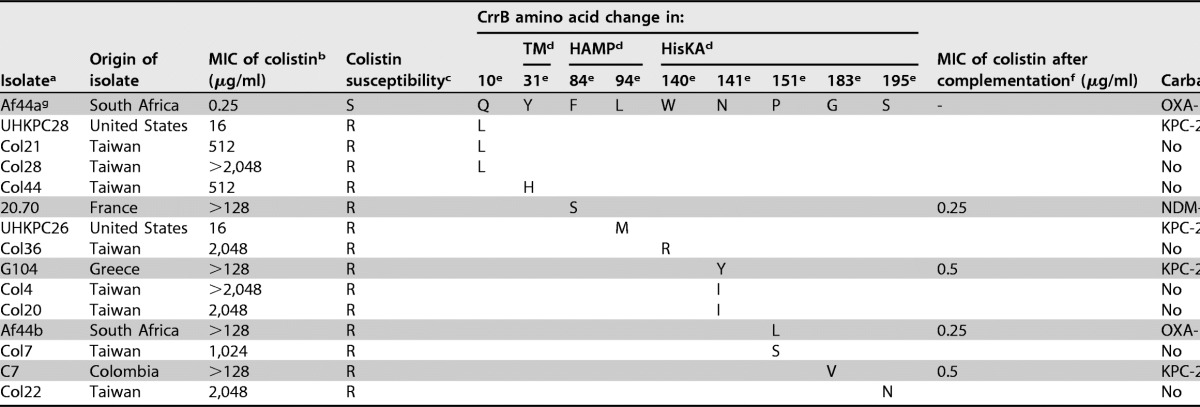
TABLE 1.
Features of colistin-resistant K. pneumoniae clinical isolates
aIsolates from this study are indicated by shading.
bMICs of colistin were determined using the manual broth microdilution reference method for this study, Etest for the study by Wright et al. (5), and agar dilution for the study by Cheng et al. (6).
cS, susceptible (MIC, ≤2 μg/ml); R, resistant (MIC, >2 μg/ml), according to EUCAST breakpoints (http://www.eucast.org/).
dDomains of the CrrB protein predicted by SMART software are indicated as follows: TM, transmembrane domain (amino acids 12–34); HAMP, histidine kinase, adenylyl cyclase, methyl binding protein, and phosphatase domain (amino acids 81–135); HisKA, histidine kinase A (phosphoacceptor) domain (amino acids 136–200).
eAmino acid positions where mutations have been detected.
fMICs of colistin after complementation with a wild-type CrrB protein (with plasmid crrB-pTRIC).
gThe colistin-susceptible isolate Af44a is the isogenic colistin-susceptible counterpart of Af44b.