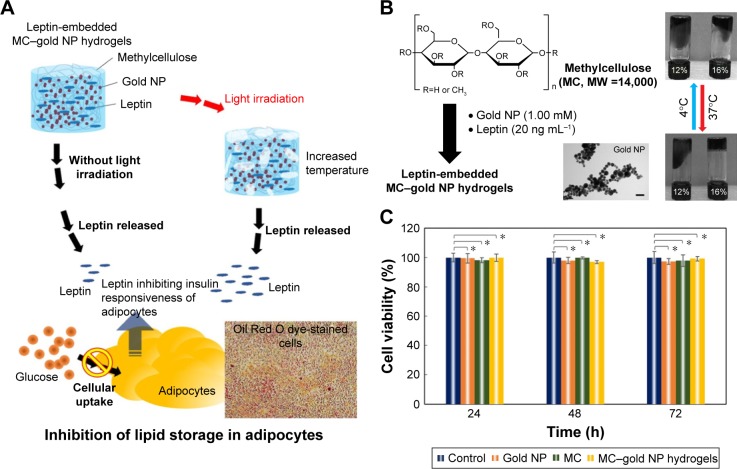
Figure 1.
Light-sensitive MC–gold NP hydrogels.
Notes: (A) A conceptual representation of a light-triggered MC–gold NP hydrogel for leptin release to inhibit fat stores in adipocytes. Light irradiation increases porosity and promotes efflux of payload material in a controlled, tunable manner. (B) Schematic illustration of the synthesis of leptin-embedded MC–gold NP hydrogels. Leptin was embedded into MC–gold NP hydrogels and exposed to 37°C for 5 min to facilitate the formation of MC–gold NP hydrogels. The TEM image is of gold NPs. Bar =50 nm. Photographs (right panel) of MC–gold NP hydrogels with 12% or 16% (v/v) MC. A complete hydrogel was achieved at 16% (v/v). (C) Viability of 3T3-L1 cells after exposure to various treatments. Cell viability is given as the percentage of viable cells remaining after treatment for 24, 48, or 72 h when compared with unexposed cells. Cell numbers were determined by the standard MTS assay (*P>0.15; based on a two-tailed t-test, assuming unequal variances). The bars represent the mean ± standard deviation (n=6).
Abbreviations: MC, methylcellulose; MTS, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium; NP, nanoparticle; TEM, transmission electron microscopy.