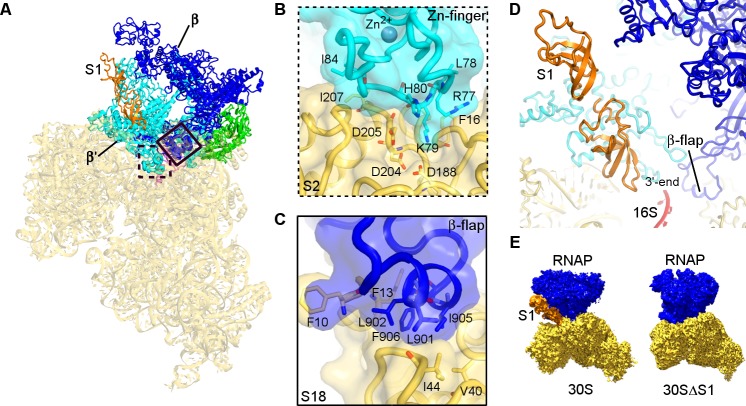
Figure 2. Structural basis for binding of RNAP to the 30S subunit.
(A). Two binding sites of RNAP (boxed). (B) Close-up view of the Zn-finger interactions with S2. (C) Close-up view of the β−flap helix packing on S18. Molecular surface, secondary structure and sticks are shown in panels (B) and (C). (D) Position of two OB domains of S1 (orange) near the 3′ end of 16S rRNA (red). (E) Comparison of segmented maps of the 30S•RNAP complex formed with and without S1.
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Crosslinked sites mapped on the 30S•RNAP structure.
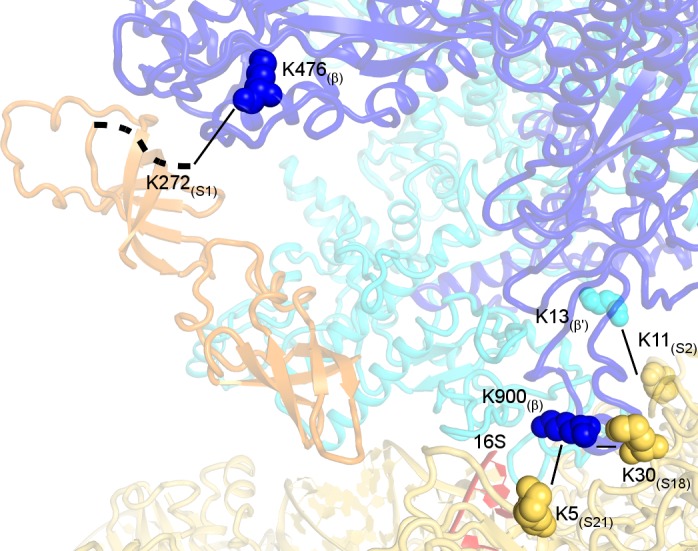
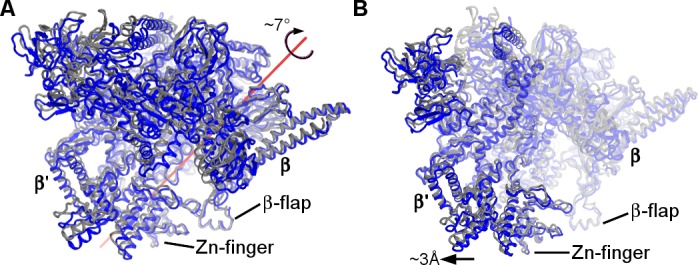
Figure 2—figure supplement 2. Conformational rearrangements of RNAP between the non-rotated (blue) and rotated (gray) states.