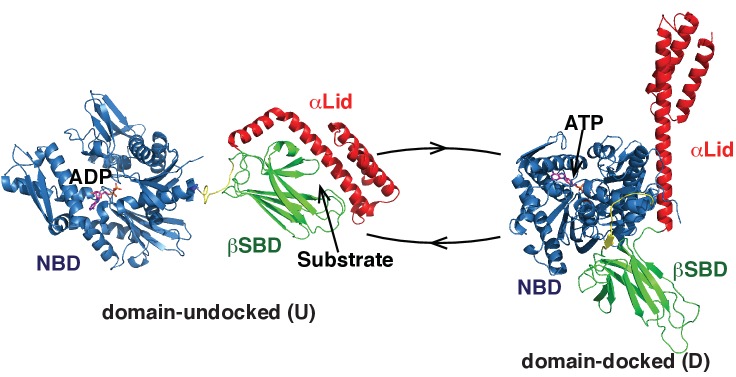
Figure 1. Two main functional conformations of BiP.
Ribbon representation of the structure of the ATP-bound BiP (PDB 5e84 [(Yang et al., 2015]), referred as the domain-docked conformation, and ADP-bound, which was modeled from the structures of the isolated NBD (PDB 5evz [Hughes et al., 2016]) and (D) SBD (PDB 5e85 [Yang et al., 2015]) and referred as the domain-undocked (U) conformation. The NBD (blue), βSBD (green), and αLid are highlighted by different colors and labeled.