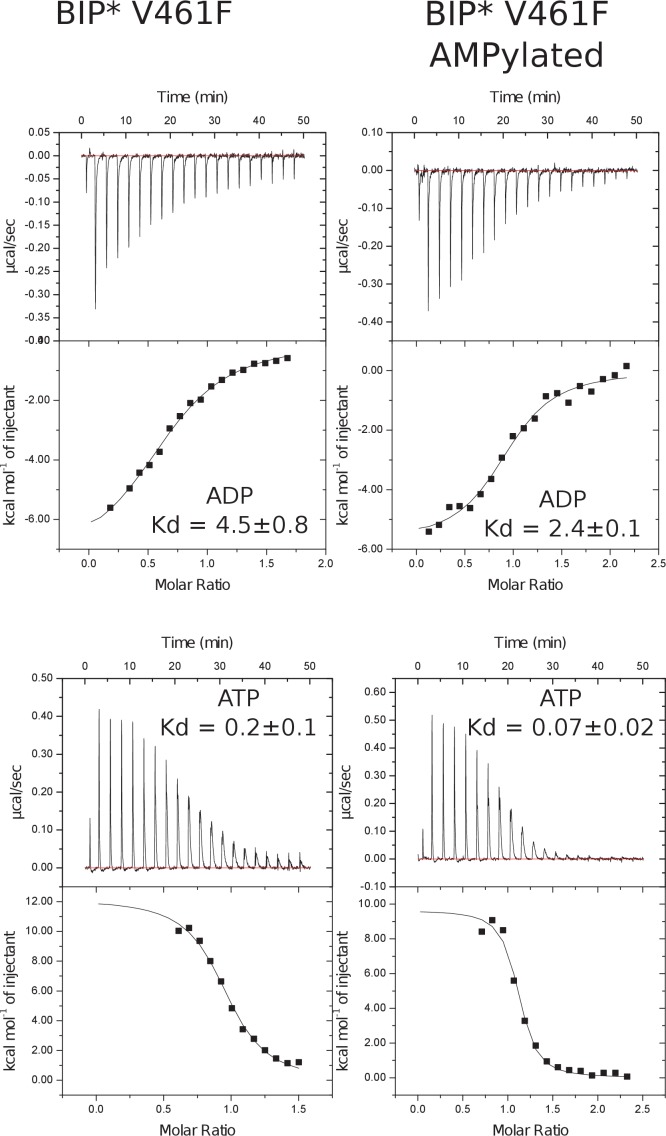
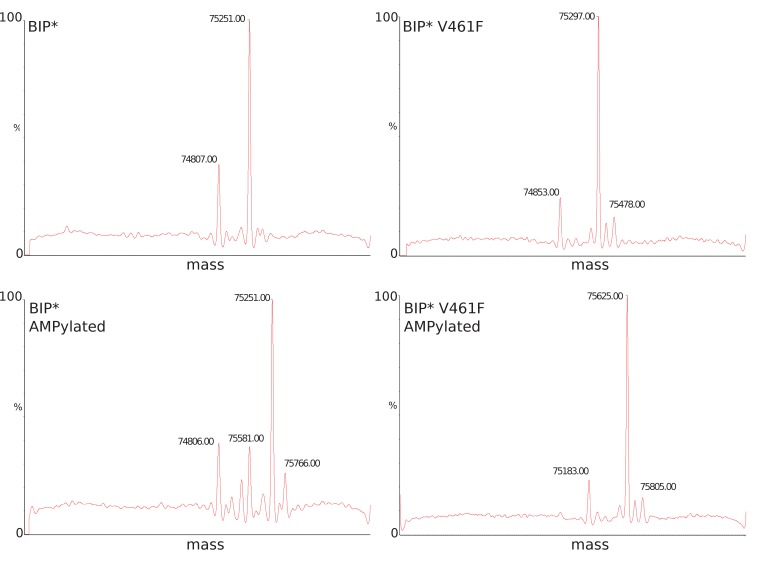
Figure 5. Allosteric regulation of the BiP by AMPylation.
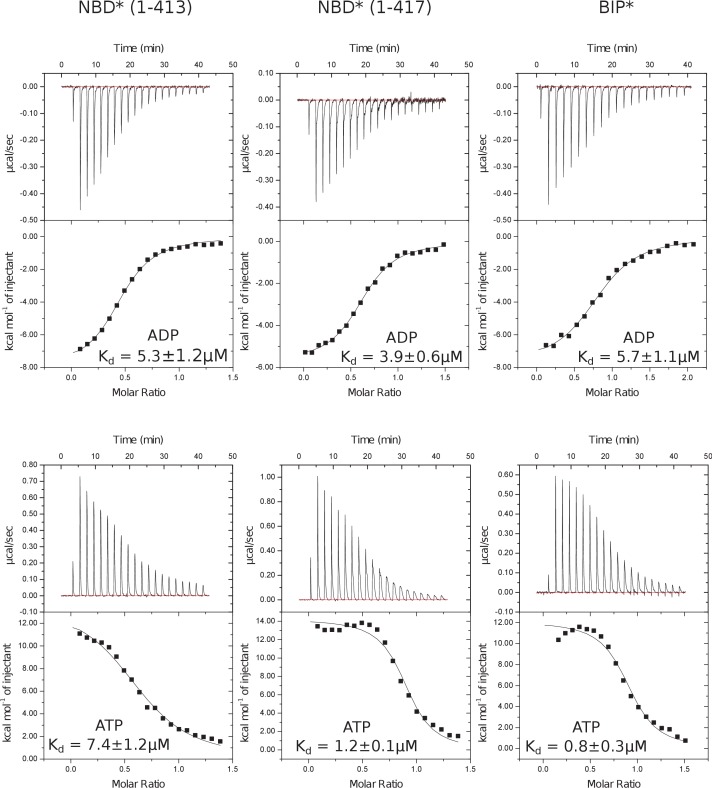
(A) Populations of the domain-docked conformation for AMPylated and non-AMPylated BiP* and its V461F variant in the presence of ATP and ADP, calculated using methyl peak intensities of the domain-docked and -undocked conformations. Error bars show SDs from the means for three peak doublets (Materials and methods, Figure 5—figure supplements 1–2 and Figure 5—source data 1). (B) The thermodynamic linkage between domain docking and nucleotide binding: Plot of the experimental free energy of ATP (red dots) and ADP (black dots) binding against the experimental free energy of domain docking for BiP* and its non-AMPylated and AMPylated V461F variant. For each construct, the free energy of nucleotide binding was obtained from the ITC data and the free energy of domain docking was calculated from NMR peak intensities (see Figure 5—source data 2 and Materials and methods for details). The red (for ATP) and black (for ADP) curves show the theoretical plots of the free energy of ATP (red) and ADP (black) binding against the free energy of domain docking under assumption that BiP co-exists as an ensemble of the domain-undocked and -docked conformations (see Materials and methods).
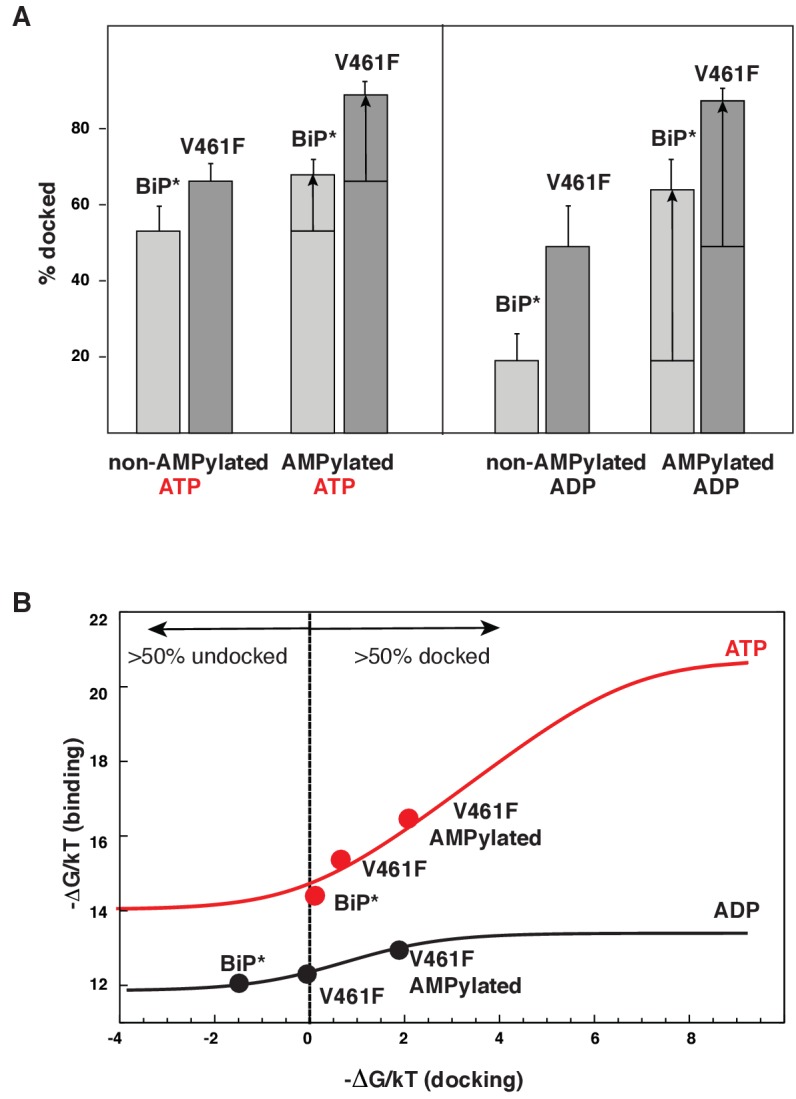
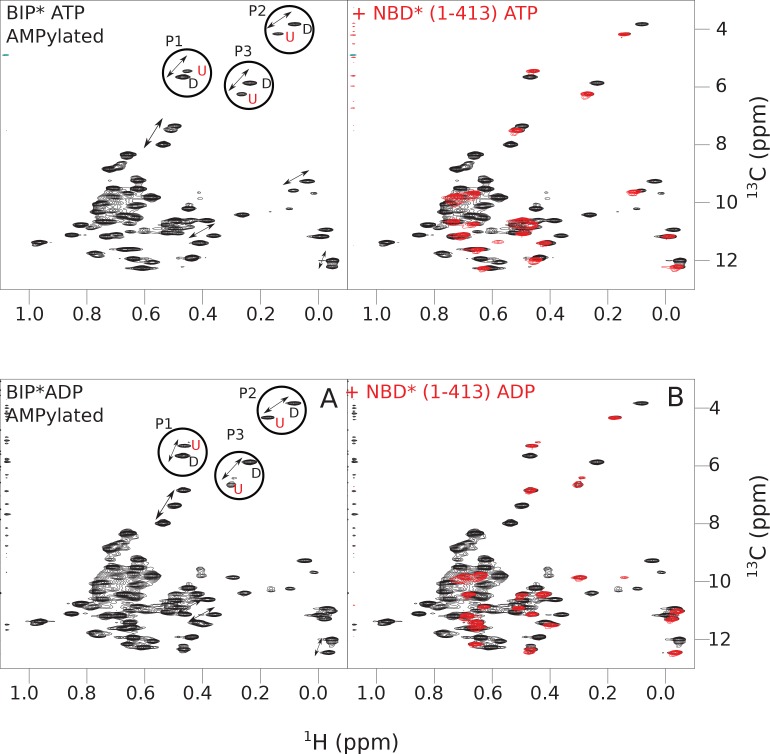
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. The isoleucine regions of methyl-TROSY spectra of ATP- and ADP-bound states of AMPylated full-length (FL) BiP* (A, in black), overlaid with the spectra of a corresponding nucleotide-bound state of NBD*(1-413) (B, in red).
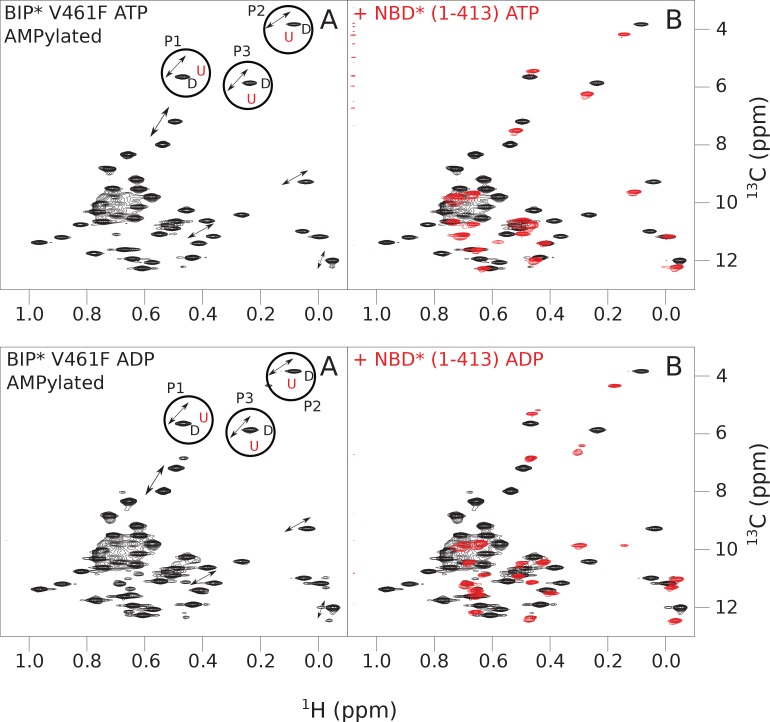
Figure 5—figure supplement 2. The isoleucine regions of methyl-TROSY spectra of ATP- and ADP-bound states of AMPylated full-length (FL) V461F BiP* (A, in black), overlaid with the spectra of a corresponding nucleotide-bound state of NBD*(1-413) (B, in red).
Figure 5—figure supplement 3. The methyl TROSY spectrum of ATP-bound AMPylated BiP*-V461F (black) overlaid with the spectrum of ADP-bound AMPylated BiP*-V461F (red).
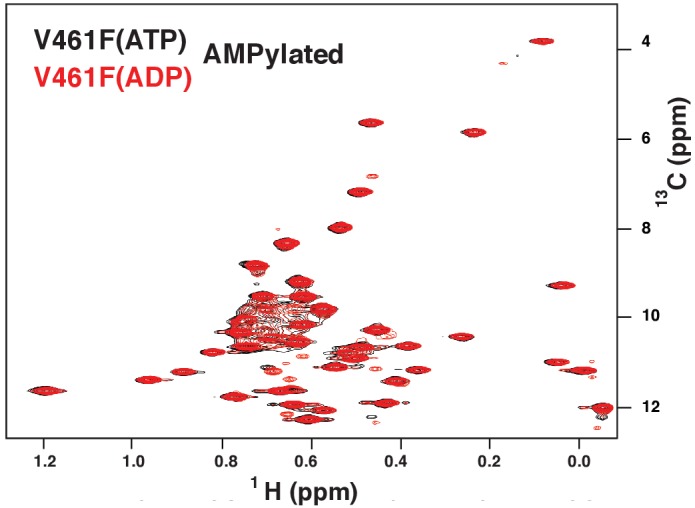
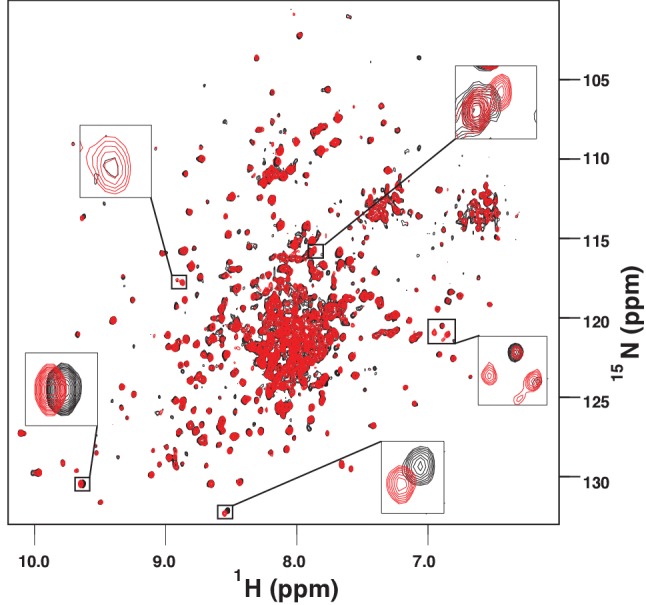
Figure 5—figure supplement 4. The amide TROSY spectrum of ATP-bound AMPylated BiP*-V461F (black) overlaid with the spectrum of ADP-bound AMPylated BiP*-V461F (red).