Figure 3. Oral PAC-1 is efficacious as a single agent in an intracranial model of glioblastoma and synergistically enhances the efficacy of TMZ in intracranial models of glioblastoma.
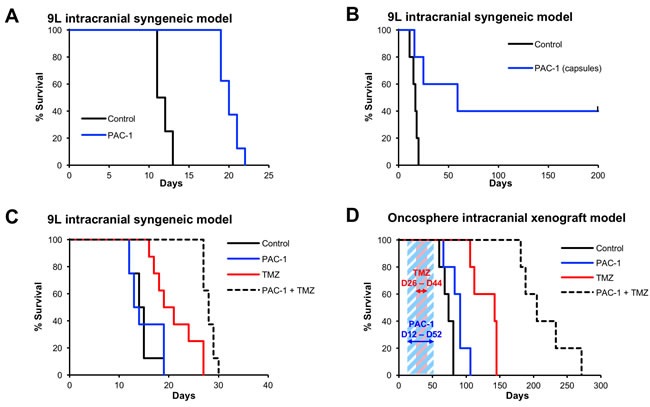
A. PAC-1 improved survival of 9L rats by 73% (p < 0.001). Rats received 10 oral doses (50 mg/kg, in an aqueous oral suspension, days 5-9 and 12-16). The median survival of control animals was 11.5 days, compared to 20 days in PAC-1 treated animals. 8 rats per group. B. PAC-1, administered in a gelatin capsules, improved survival of 9L rats by 350% (p = 0.02), from 17 days to 59 days. Rats received 16 oral doses (50 mg/kg, solid packed into size 9 capsules, days 3-18). 5 rats per group. C. Combinations of PAC-1 and TMZ synergistically extend survival in intracranial 9L rat glioblastoma. PAC-1 (50 mg/kg, administered in an aqueous oral suspension, days 1-5), did not improve survival as a single agent (median survival 13.5 days compared to 14.5 days in the control group), but did extend survival when used in combination with TMZ (50 mg/kg, oral, days 6-10; TMZ alone median survival: 20 days, PAC-1 + TMZ median survival: 28 days). The combination of PAC-1 + TMZ extended survival to a statistically significant extent compared to control rats (p < 0.0001) and TMZ as a single agent (p = 0.007). 8 rats per group. D. Combinations of PAC-1 and TMZ synergistically extend survival in intracranial oncosphere-derived glioblastoma (cell line 020913) in NOD SCID mice. PAC-1 (50 mg/kg, oral, 5 days a week from day 12-52, shown with blue diagonal shading) improved survival from 74 days (control) to 91 days (p = 0.034). TMZ alone (50 mg/kg, oral, 5 days a week from day 26-44, shown with red diagonal shading) improved survival to 142 days. The combination of PAC-1 and TMZ was most effective, extending the median survival to 205 days (p = 0.0027 compared to TMZ, p < 0.0001 compared to control). 5 mice per group.
