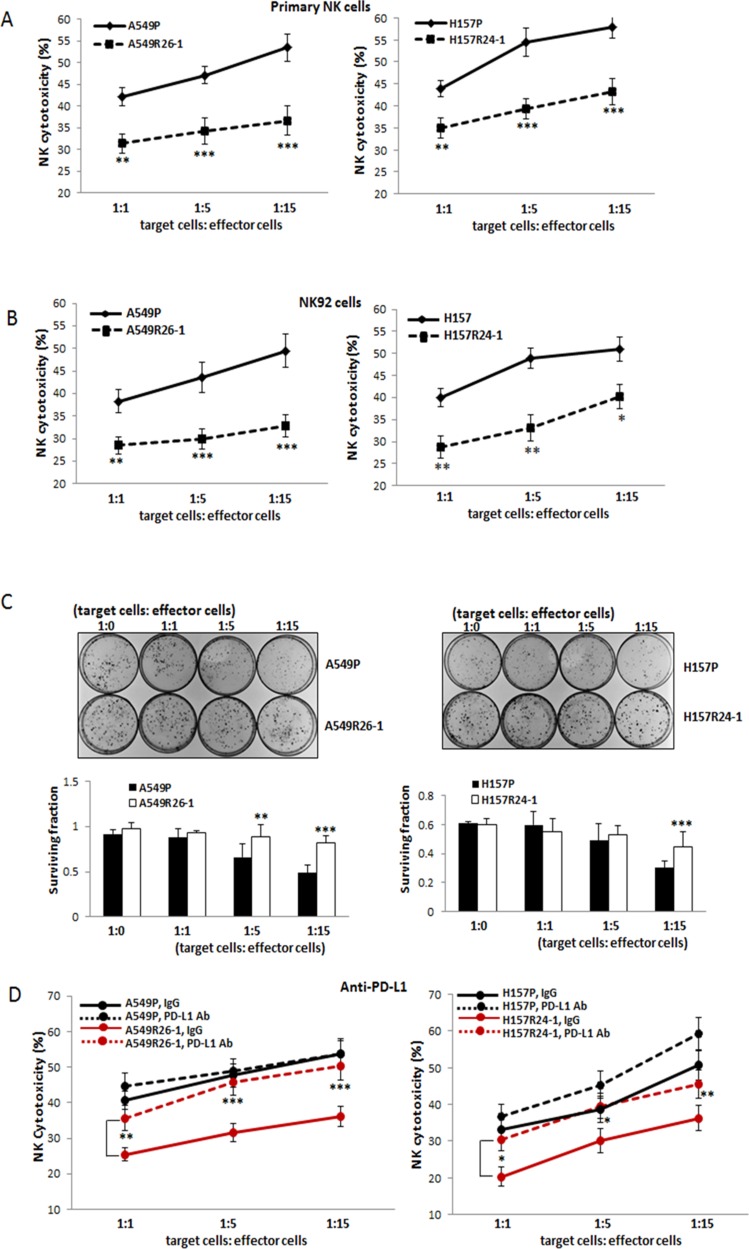
Figure 3. Tests of susceptibilities of radioresistant cells vs. parental cells to NK cell cytotoxicity.
(A, B) NK-cell cytotoxicity tests using primary NK cells (A) and NK92 cells (B). The susceptibilities of A549P/A549R26-1 and H157P/H157R24-1 cells to NK cell cytotoxicity were tested in LDH release-based cytotoxicity test kit. The experimental release was corrected by subtraction of the spontaneous release of effector cells at corresponding dilutions. Left panels show data of A549P/A549R26-1 cell set and right panels show data of H157P/H157R24-1 cell set. (C) Colony formation assay. The surviving A549P/A549R26-1 and H157P/H157R24-1 cells after NK cell incubation (4 hours) were grown. The colonies were stained with Crystal Violet and the colony numbers were counted under microscopy. (D) NK cell cytotoxicity test after adding PD-L1 Ab (matched IgG as control) to tumor/NK cells co-culture. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001