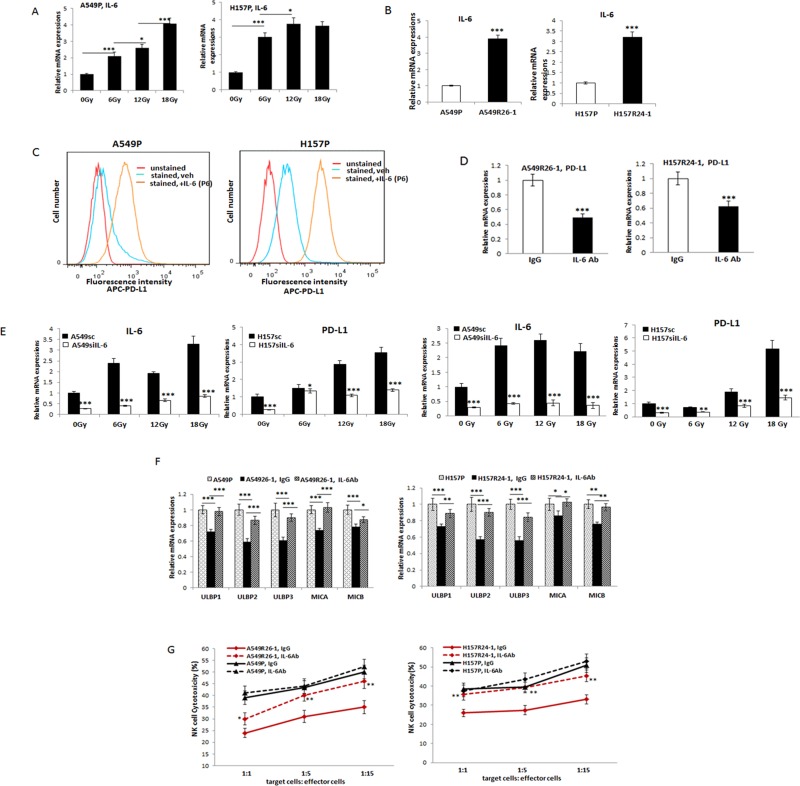
Figure 4. Investigations on the implication of IL-6 signaling in altering PD-L1/NKG2D ligand levels in lung cancer cells and its influence on NK cell cytotoxicity to tumor cells.
(A) qPCR analyses of IL-6 levels in A549 and H157 cells after radiation. (B) IL-6 levels (mRNA) in parental and radioresistant cells. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of surface PD-L1 levels on A549 and H157 cells after treating with IL-6 (P6; passage 6 in the presence of IL-6, 10 ng/ml). (D) PD-L1 level in A549R26-1 and H157R24-1 cells after treating cells with IL-6 Ab (IgG as control). (E) qPCR analyses of PD-L1 in A549siIL-6/sc and H157siIL-6/sc cell sets after radiation IL-6 knocked down (siIL-6) and scramble (sc) control cells were treated with radiation (6, 12, and 18 Gy total) and PD-L1 levels were analyzed by qPCR analyses. (F) NKG2D ligand levels in A549R26-1 and H157R24-1 cells after treating cells with IL-6 Ab (IgG as control). (G) NK cell cytotoxicity test to A549R26-1 and H157R24-1 cells after adding IL-6 Ab to the co-culture of tumor/NK cells. Primary NK cells were used in this assay. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.