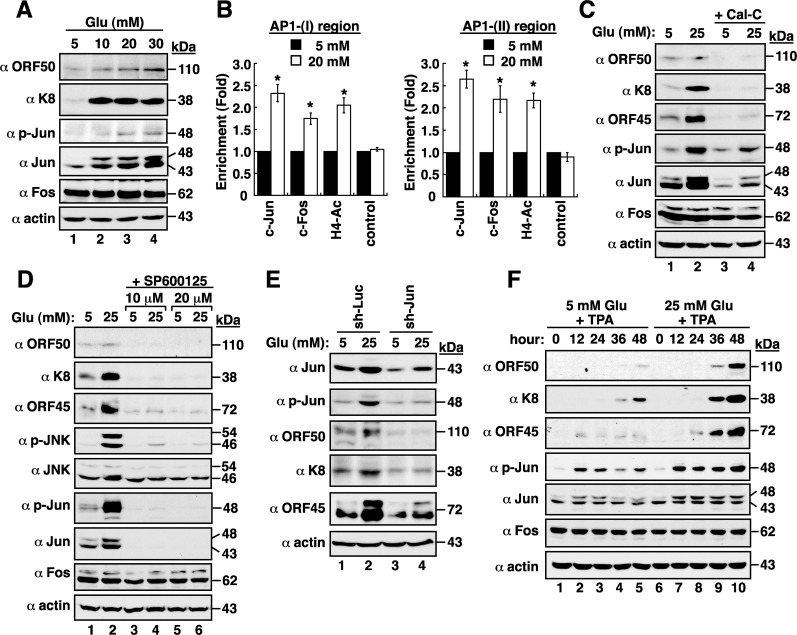
Figure 5. High glucose activates AP1 transcription factor in BCBL1 cells.
(A) Expressions of viral and cellular proteins in BCBL1 cells that were cultured at different glucose concentrations. (B) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays were performed to evaluate the binding of c-Jun, c-Fos, or acetyl-histone H4 to the AP1-(I)- or AP1-(II)-containing region of the ORF50 promoter in normal and high-glucose cultured BCBL1 cells. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (n=3). Symbol * represents significant difference vs. the normal glucose treatment (P < 0.05). (C) Effect of calphostin C, a PKC inhibitor, on viral reactivation. BCBL1 cells that were untreated or treated with calphostin C (Cal-C; 0.25 μM) were cultured in media containing normal or high glucose (25 mM) for 2 days. The treated samples were subjected to Western blot analysis. (D) Effect of SP600125, a JNK inhibitor, on high glucose-mediated viral reactivation. SP600125 at a concentration of 10 μM or 20 μM was used to treat BCBL1 cells for 2 days under normal or high glucose (25 mM) conditions. (E) Effect of c-Jun knockdown on high glucose-mediated viral reactivation. BCBL1 cells that were infected with lentivirus encoding shRNA to luciferase (Luc) or to c-Jun were cultured in normal or high glucose conditions. At 24 hr after lentiviral infection, cells were harvested and analyzed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. (F) Time course analysis of AP1 components and viral lytic proteins expressed in TPA-induced BCBL1 cells that were exposed to normal or high glucose.