Table 2. Summary of ERβ-selective compounds that have been reported to be of treatment effect on malignant gliomas.
| Compound | Origin | Chemical structure | Most recent results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liquiritigenin | Glycyrrhiza uralensis | 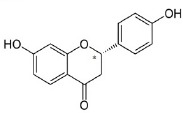 |
Liquiritigenin has the potential to inhibit glioma cell proliferation in vitro and also in vivo in xenograft-based assays. | Sareddy et al. (2012) |
| DPN | Synthetic | 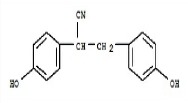 |
Treatment of glioma cells with DPN resulted in a significant dose-dependent reduction in cell proliferation | Sareddy et al. (2012) |
| Monoaryl-substituted salicylaldoxime | Synthetic | 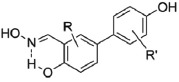 |
These deries of compounds were found to inhibit glioma growth in vitro were proved to be active in an in vivo xenograft model of human glioma, thus demonstrating the high potential of this type of compounds against malignant gliomas. | Paterni et al. (2015) |
| TSN | Melia toosendan Sieb. et Zucc. | 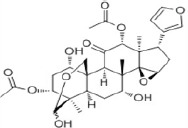 |
TSN is a candidate of novel anti-cancer drugs for malignant glioma and ER β and p53 were prominent targets for TSN. |
Cao et al. (2016) |
| LY500307 | Synthetic | 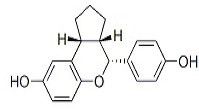 |
LY500307 treatment significantly reduced the in vivo tumor growth and promoted apoptosis of glioblastoma tumors in an orthotopic model and improved the overall survival of tumor-bearing mice. | Sareddy et al. (2016) |
Abbreviations: DPN: 2,3-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-propionitrile; TSN: Toosendanin.
