Fig 7. Membrane phase space near repolarization point.
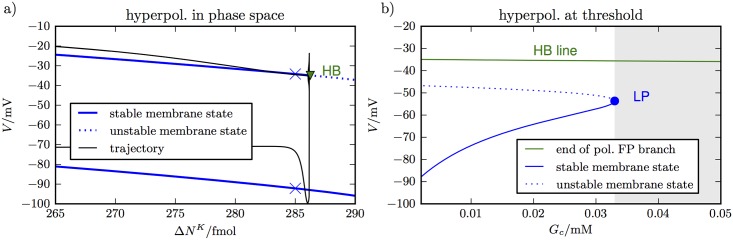
Panel (a) shows the stable and unstable fixed points of the membrane model as ΔNK varies for extremely low Gc (set to 0.0001 mM as in Fig 2). There is a stable depolarized and a stable (hyper–)polarized state. At the repolarization point (triangle marker) the depolarized state becomes unstable. The trajectory is guided by the fixed point branches and gets close to the lower branch before ion concentrations adjust and the neuron approaches a level slightly above the lower branch. A de– and a hyperpolarized state close to but before repolarization are marked. The values are given in Table D in S1 Text. Panel (b) shows the potentials at the ends of the upper fixed point branches for all Gc–values between 0 and 0.05 mM. The other membrane fixed point states, stable hyperpolarization, and an unstable state, are also shown. The stable hyperpolarized state ceases to exist for Gc–values higher than 0.32 mM. Beyond this critical value repolarization is no longer possible (shaded region). The critical value is consistent with the value we have derived for the transmembrane model in Fig 6.