Figure 5.
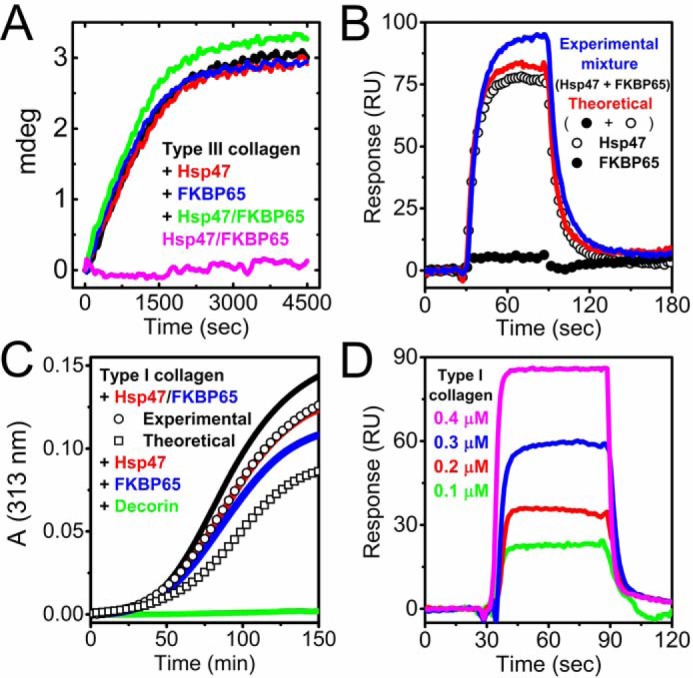
The effect of FKBP65 on collagen folding in the presence of Hsp47. A, kinetics of the refolding of full-length type III collagen in the presence of Hsp47 and/or FKBP65 monitored by CD at 220 nm is shown. The concentration of type III collagen, FKBP65, and Hsp47 were all 0.2 μm. The refolding curves shown are in the absence (black) and presence of Hsp47 (red) and FKBP65 (blue). The mixture of Hsp47 and FKBP65 with (green) and without (magenta) type III collagen are also shown. B, SPR analysis was carried out using a BIAcore X instrument to determine the binding orientation of Hsp47 and FKBP65 to the collagen chip. The open and closed circles are Hsp47 (0.05 μm) and FKBP65 (0.2 μm), respectively. Red and blue curves indicate the theoretical signal derived from the addition of individual Hsp47 and FKBP65 curves and the experimental curve from a mixture of both Hsp47 and FKBP65, respectively. C, fibril formation of type I collagen. A stock solution of type I collagen in 50 mm acetic acid was diluted to a final concentration of 0.1 μm. Fibril formation in the absence (black) and presence of 0.2 μm Hsp47 (red) and 0.2 μm FKBP65 (blue) is shown. 0.2 μm decorin was used as a positive control (green). The squares and circles indicate the theoretical signal derived from the addition of individual FKBP65 and Hsp47 signals, and the experimental signal from a mixture of FKBP65 and Hsp47, respectively. D, direct binding kinetics were measured by SPR analysis using a BIAcore X instrument. Various concentrations of pepsin-treated type I collagen were run over the FKBP65 chip. The following binding curves are shown: 0.1 μm (green), 0.2 μm (red), 0.3 (blue) and 0.4 μm (magenta) Hsp47. All curves in A–D are averaged by a minimum of three measurements. These results indicate that FKBP65 preferentially interacts with Hsp47 rather than type I collagen, and the interaction between Hsp47 and FKBP65 creates a synergistic function for collagen folding.
