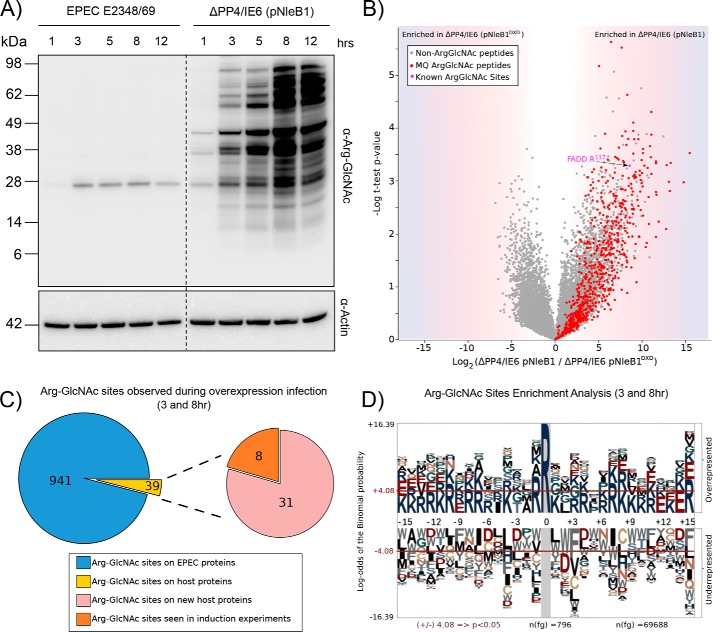
Figure 3.
Overexpression of NleB1 results in non-authentic modifications of both bacterial and host substrates. A, time course of EPEC E2348/69 infection over 12 h shows extensive arginine GlcNAcylation when NleB1 is overexpressed compared with wild-type EPEC E2348/69 infections. B, label-free quantification of Arg-GlcNAc peptide pulldown results from 8-h infection of HT-29 cells with EPEC E2348/69 ΔPP4/IE6 (pNleB1) versus EPEC E2348/69 ΔPP4/IE6 (pNleB1DXD). The scatter plot shows the mean ion intensity peptide ratios of E232489/69 ΔPP4/IE6 (pNleB1) versus E2348/69 ΔPP4/IE6 (pNleB1DXD) plotted against negative logarithmic t test p values from biological triplicate experiments. Within biological replicates of EPEC E2348/69 ΔPP4/IE6 (pNleB1) infections, multiple putative arginine-GlcNAcylated peptides were enriched from both bacterial and host origin (colored in red) with Arg-GlcNAc peptides containing previously known Arg-GlcNAc modifications shown in purple. MQ, MaxQuant. C, Arg-GlcNAc sites observed within EPEC E2348/69 ΔPP4/IE6 (pNleB1) infections are predominantly derived from bacterial origin with the host proteins modified during infection identical to those seen during stable NleB1 induction. D, pLogo motif analysis of Arg-GlcNAc sites observed within EPEC E2348/69-derived proteins. Arg-GlcNAc sites are flanked by basic residues.