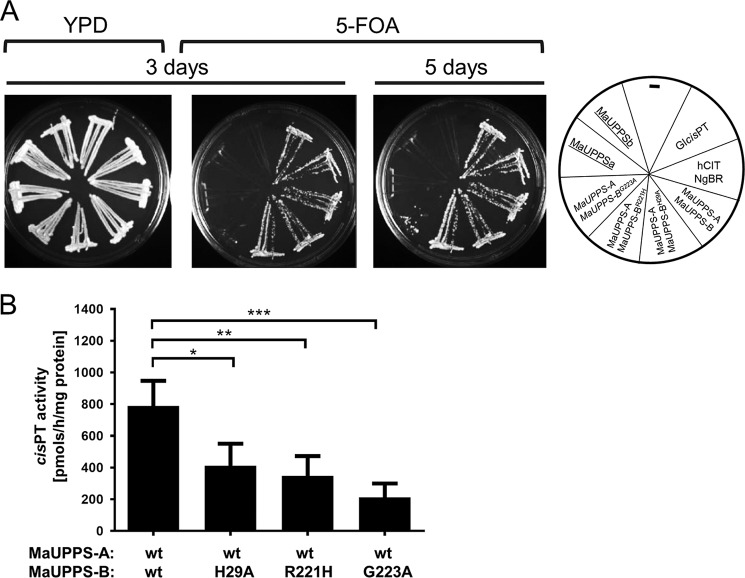
Figure 7.
Phenotypical and biochemical analysis of heteromeric MaUPPS supports predicted length of cis-PT domain of NgBR and importance of C-terminal RXG motif. A, the rer2Δ, srt1Δ, nus1Δ triple deletion strain expressing G. lamblia cis-PT from URA3 plasmid was co-transformed with the LEU2 and MET15 plasmids bearing wild-type or mutated variant of MaUPPS-A (hCIT/Rer2/Srt1 ortholog) and MaUPPS-B (NgBR/Nus1 ortholog) as indicated. Cells transformed with empty plasmid were used as negative control, and cells transformed with LEU2 Glcis-PT or co-transformed with hCIT (LEU2) and NgBR (MET15) were used as positive control. The cells were streaked onto YPD or synthetic complete medium containing 1% FOA. The growth of cells was monitored overtime to assess phenotypic differences. The combination of alleles affecting the growth is indicated in italics, and the combination not supporting the growth is underlined. B, cis-PT activity was measured using S. cerevisiae rer2Δ, srt1Δ, nus1Δ membrane fractions expressing WT or mutated MaUPPs subunits as indicated. The data are means ± S.D. values of four or five replicates in two independent experiments.