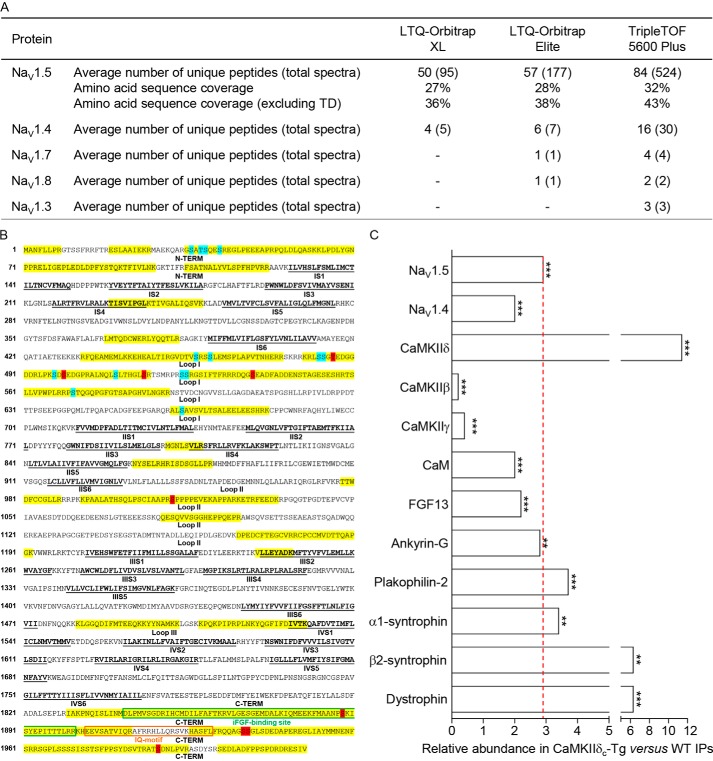
Figure 2.
MS protein identification in immunoprecipitated NaV channel complexes from WT and CaMKIIδc-Tg mouse ventricles. A, NaV α subunits identified using the LTQ-Orbitrap XL, LTQ-Orbitrap Elite, and TripleTOF 5600 Plus mass spectrometers. The average numbers of exclusive unique peptides and total spectra for each NaV α subunit and the percent amino acid sequence coverages obtained for NaV1.5, including or excluding transmembrane domains (TD), are presented. In addition to NaV1.5, which is the most abundant protein in the mαNaVPAN-IPs, NaV1.4 is also detected, and the greater sensitivity of the Orbitrap Elite and TripleTOF mass spectrometers allowed the identification of NaV1.7, NaV1.8, and NaV1.3. B, amino acid sequence coverage obtained for the (mouse) NaV1.5 protein (NP_001240789). Detected peptides are highlighted in yellow; identified phosphorylation sites are highlighted in blue (sites already identified in our previous MS analyses) and red (newly identified sites in the present study); transmembrane segments (S1–S6) in each domain (I–IV) are in bold and underlined in black; loops I, II, and III correspond to interdomains I and II, II and III, and III and IV, respectively; and binding sites for iFGF and calmodulin (IQ-motif) are boxed in green and orange, respectively. C, relative abundances of NaV α subunits and previously characterized NaV1.5 channel-associated/regulatory proteins in the CaMKIIδc-Tg IPs (n = 4) versus the WT IPs (n = 4) were calculated from the entire (Orbitrap XL) MS1 peptide data set using the DAnTE statistical software (**, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001).