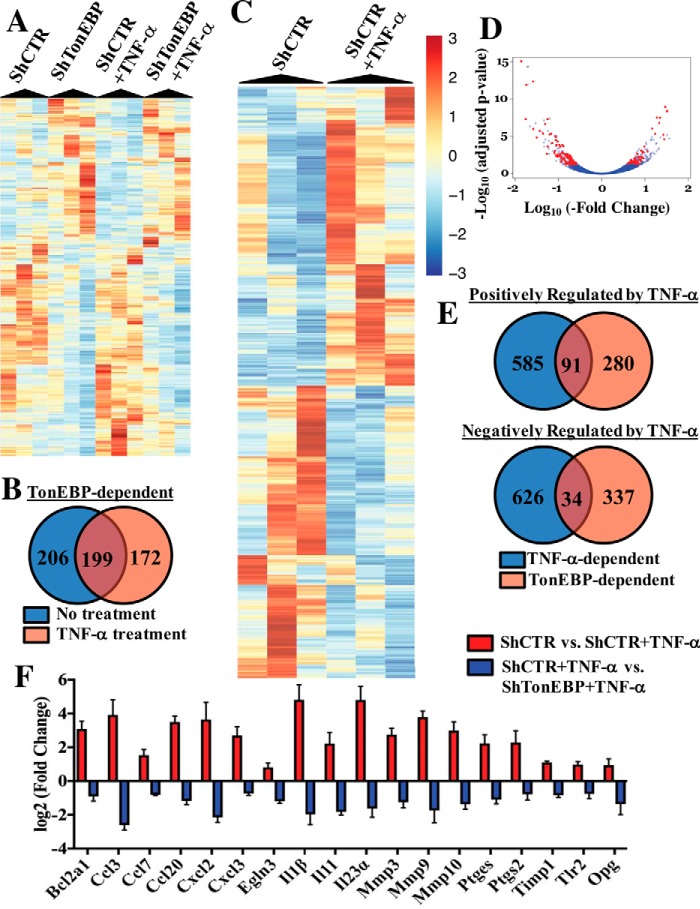
Figure 3.
RNA sequencing reveals TonEBP as an important regulator of NP cell response to TNF-α. NP cells were transduced with either ShControl or ShTonEBP and cultured with or without TNF-α for 24 h, and RNA sequencing was performed. A, heat map depicting genes differentially expressed between shControl and shTonEBP under either basal or TNF-α-stimulated (24-h TNF-α) conditions. B, Venn diagram showing overlap between TonEBP-dependent genes in untreated versus TNF-α-treated cells. C, heat map depicting genes differentially expressed between control and TNF-α treatment groups. D, volcano plot depicting expression of transcripts that are differentially expressed between control and TNF-α treatment groups and controlled by TonEBP under TNF-α treatment. E, Venn diagrams showing overlap between genes positively or negatively regulated by TNF-α and also regulated by TonEBP. F, log2(−fold change) values for inflammation-related transcripts that were differentially expressed between control and TonEBP knockdown under TNF-α treatment; genes shown were statistically significant between the indicated experimental groups, as defined by adjusted p value <0.05. Quantitative measurements represent mean ± S.E. of ≥3 biological replicates.