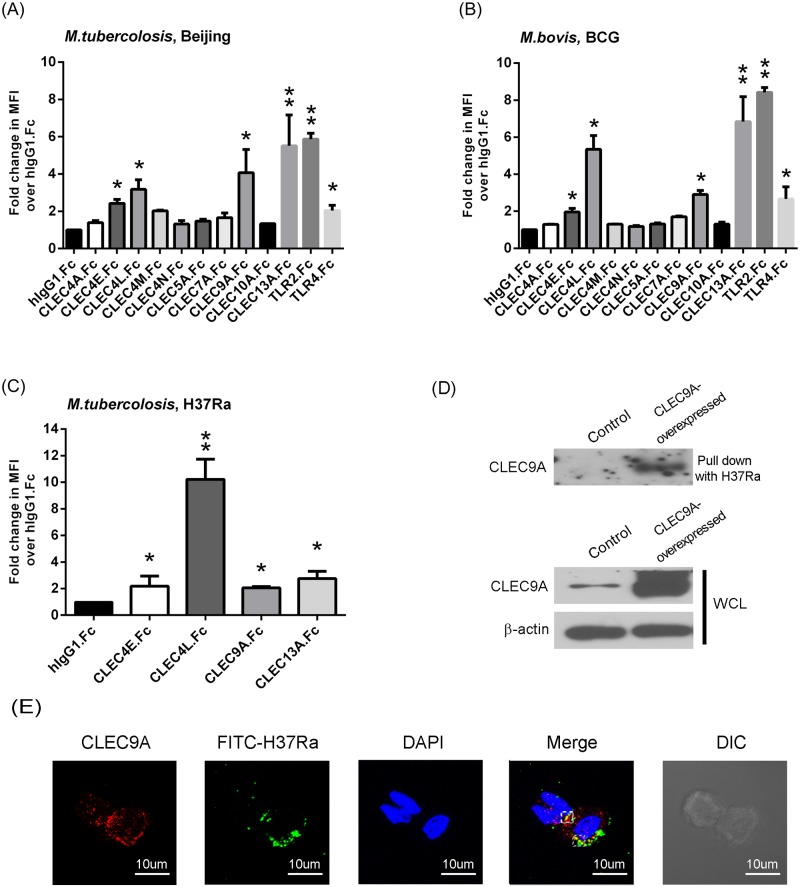
Fig 1. CLEC9A is identified as a novel candidate that is able to bind with mycobacteria.
Interaction of heat-killed (A) M. tuberculosis Beijing, (B) M. bovis BCG and (C) M. tuberculosis H37Ra with human receptor-Fc fusion protein was determined by flow cytometry. Human IgG1 was used as a negative control. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. Data were expressed as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Two-tailed multiple t-tests were performed (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01). (D) The pull-down assay for CLEC9A using H37Ra. H37Ra was incubated with cell lysate from control or CLEC9A-overexpressing HEK293T cells. After washing and gel-separation, the interaction of H37Ra with CLEC9A was detected by immunoblotting. (E) The membrane localization of H37Ra and CLEC9A was analyzed by confocal microscopy. The THP-1 cells were incubated with FITC-labeled H37Ra for 1 hour, fixed, and stained with antibody against CLEC9A and DAPI. Representative confocal images of three independent experiments is shown.