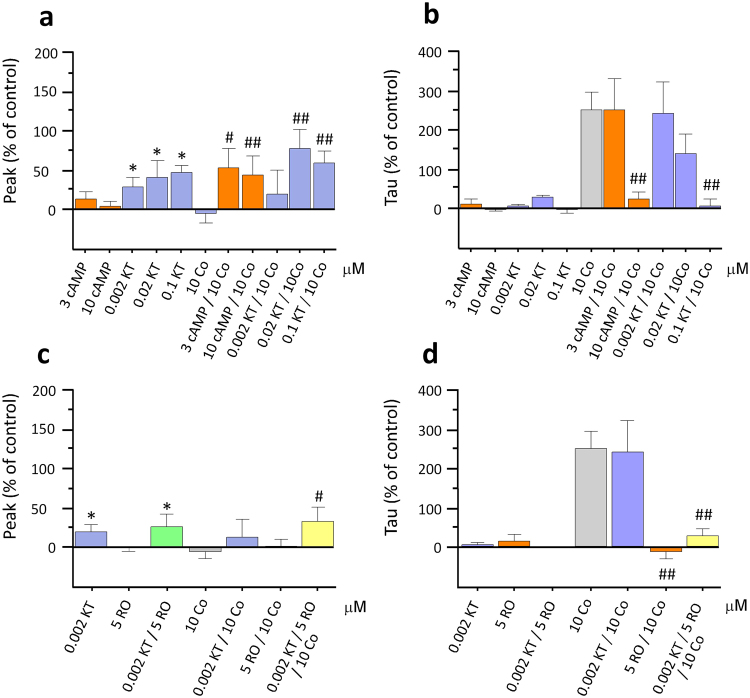
Figure 3.
Effects of PKA inhibition and activation on cocaine-induced changes in DA transmission. Co-application of 10 μM cocaine (Co) with either a PKA activator (cAMP) or an inhibitor (KT 5720; KT) resulted in a significant increase in DA release (a). KT also caused a significant increase in peak DA in comparison to baseline values when perfused alone (a). Superfusing cocaine with either 10 μM cAMP or 0.1 μM KT significantly attenuated cocaine-induced increases in tau (b). Perfusion of the lowest concentration of KT, which had no effect on DA clearance in its own right, in the presence of both 5 μM RO5256390 and 10 μM cocaine, had no effect on RO5256390’s ability to attenuate cocaine-induced increases in tau (d). (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs baseline; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 vs cocaine values; n = 5–19).